The significance and regulatory mechanisms of innate immune cells in the development of sepsis
- PMID: 24006870
- PMCID: PMC3887438
- DOI: 10.1089/jir.2013.0042
The significance and regulatory mechanisms of innate immune cells in the development of sepsis
Abstract
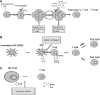
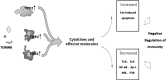
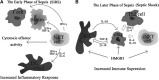
Sepsis with subsequent multiple organ dysfunction is a pronounced systemic inflammatory response to concealed or known infection and is a leading cause of death in intensive care units. The survival rate of severe sepsis and septic shock has not markedly improved in recent decades despite a great number of receptors and molecules involved in its pathogenesis have been found and taken as therapeutic targets. It is essential to thoroughly understand the host cell-mediated immunity involved in the development of sepsis and sepsis-related organ injury. Recent studies indicate that innate immune cells (such as neutrophils, macrophages, dendritic cells, T lymphocytes, regulatory T cells, and natural killer T cells) play pivotal roles in the maintenance of peripheral homeostasis and regulation of immune responses during sepsis. Therefore, an understanding of the biological significance and pathophysiological roles of different cell populations might gain novel insights into the immunoregulatory mechanisms of sepsis. In this review, we focus on major immune cells that may play potential roles in the contribution of new therapeutic approaches for sepsis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Host immunosuppression in pathogenesis of sepsis and its clinical implication].Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2007 Mar;19(3):138-41. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2007. PMID: 17376264 Chinese.
-
Insights into the apoptotic death of immune cells in sepsis.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015 Jan;35(1):17-22. doi: 10.1089/jir.2014.0069. Epub 2014 Jul 9. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015. PMID: 25007137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Precision evaluation of immune status and its significance in sepsis after burns or trauma].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2018 Nov 20;34(11):786-789. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2018.11.013. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30481919 Chinese.
-
Innate lymphocyte subsets and their immunoregulatory roles in burn injury and sepsis.J Burn Care Res. 2007 May-Jun;28(3):365-79. doi: 10.1097/BCR.0B013E318053D40B. J Burn Care Res. 2007. PMID: 17438501 Review.
-
[Cells with immunoregulatory properties and their impact in the pathogenesis of sepsis].Rev Chilena Infectol. 2011 Dec;28(6):572-8. Epub 2012 Jan 5. Rev Chilena Infectol. 2011. PMID: 22286681 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Agaricus brasiliensis Mushroom Protects Against Sepsis by Alleviating Oxidative and Inflammatory Response.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 1;11:1238. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01238. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32714320 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosuppression in Sepsis: Biomarkers and Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators.Biomedicines. 2024 Jan 13;12(1):175. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010175. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38255280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Olaparib attenuates sepsis-induced acute multiple organ injury via ERK-mediated CD14 expression.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Sep;246(17):1948-1958. doi: 10.1177/15353702211015620. Epub 2021 May 29. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 34053236 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of immune-related genes in diagnosing retinopathy of prematurity with sepsis through bioinformatics analysis and machine learning.Front Genet. 2023 Nov 10;14:1264873. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1264873. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 38028617 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of potential genes for the diagnosis of sepsis by bioinformatics and 2-sample Mendelian randomization study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jul 19;103(29):e38917. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038917. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39029061 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akdis M, Akdis CA. 2007. Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 119(4):780–791 - PubMed
-
- Alves-Filho JC, Spiller F, Cunha FQ. 2010. Neutrophil paralysis in sepsis. Shock 34Suppl 1:15–21 - PubMed
-
- Amodio G, Renna M, Paladino S, Venturi C, Tacchetti C, Moltedo O, Franceschelli S, Mallardo M, Bonatti S, Remondelli P. 2009. Endoplasmic reticulum stress reduces the export from the ER and alters thearchitecture of post-ER compartments. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41(12):2511–2521 - PubMed
-
- Annane D, Sebille V, Charpentier C, Bollaert PE, Francois B, Korach JM, Capellier G, Cohen Y, Azoulay E, Troché G. 2002. Effect of treatment with low doses of hydrocortisone and fludrocortisone onmortality in patients with septic shock. JAMA 288(7):862–871 - PubMed
-
- Bach JF. 2003. Regulatory T cells under scrutiny. Nat Rev Immunol 3(3):189–198 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

