A visual-search model observer for multislice-multiview SPECT images
- PMID: 24007181
- PMCID: PMC3772942
- DOI: 10.1118/1.4818824
A visual-search model observer for multislice-multiview SPECT images
Abstract
Purpose: Mathematical model observers are intended for efficient assessment of diagnostic image quality, but model-observer studies often are not representative of clinical realities. Model observers based on a visual-search (VS) paradigm may allow for greater clinical relevance. The author has compared the performances of several VS model observers with those of human observers and an existing scanning model observer for a study involving nodule detection and localization in simulated Tc-99m single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) lung volumes.
Methods: A localization receiver operating characteristic (LROC) study compared two iterative SPECT reconstruction strategies: an all-corrections (AllC) strategy with compensations for attenuation, scatter, and distance-dependent camera resolution and an "RC" strategy with resolution compensation only. Nodules in the simulation phantom were of three different relative contrasts. Observers in the study had access to the coronal, sagittal, and transverse displays of the reconstructed volumes. Three human observers each read 50 training volumes and 100 test volumes per reconstruction strategy. The same images were analyzed by a channelized nonprewhitening (CNPW) scanning observer and two VS observers. The VS observers implemented holistic search processes that identified focal points of Tc-99m uptake for subsequent analysis by the CNPW scanning model. The level of prior knowledge about the background structure in the images was a study variable for the model observers. Performance was scored by area under the LROC curve.
Results: The average human-observer performances were respectively 0.67 ± 0.04 and 0.61 ± 0.03 for the RC and AllC strategies. Given approximate knowledge about the background structure, both VS models scored 0.69 ± 0.08 (RC) and 0.66 ± 0.08 (AllC). The scanning observer reversed the strategy ranking in scoring 0.73 ± 0.08 with the AllC strategy and 0.64 ± 0.08 with the RC strategy. The VS observers exhibited less sensitivity to variations in background knowledge compared to the scanning observer.
Conclusions: The VS framework has the potential to increase the clinical similitude of model-observer studies and to enhance the ability of existing model observers to quantitatively predict human-observer performance.
Figures




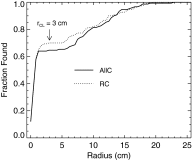
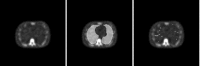

Similar articles
-
Visual-search observers for assessing tomographic x-ray image quality.Med Phys. 2016 Mar;43(3):1563-75. doi: 10.1118/1.4942485. Med Phys. 2016. PMID: 26936739 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of scatter compensation strategies for (67)Ga SPECT using numerical observers and human LROC studies.J Nucl Med. 2004 May;45(5):802-12. J Nucl Med. 2004. PMID: 15136630
-
Efficient visual-search model observers for PET.Br J Radiol. 2014 Jul;87(1039):20140017. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20140017. Epub 2014 May 16. Br J Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24837105 Free PMC article.
-
A Multiclass Model Observer for Multislice-Multiview Images.IEEE Nucl Sci Symp Conf Rec (1997). 2006;3:1687-1691. doi: 10.1109/NSSMIC.2006.354223. IEEE Nucl Sci Symp Conf Rec (1997). 2006. PMID: 19194524 Free PMC article.
-
Model observers in medical imaging research.Theranostics. 2013 Oct 4;3(10):774-86. doi: 10.7150/thno.5138. Theranostics. 2013. PMID: 24312150 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deep-learning-based model observer for a lung nodule detection task in computed tomography.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2020 Jul;7(4):042807. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.7.4.042807. Epub 2020 Jun 30. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2020. PMID: 32647740 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Inter-laboratory comparison of channelized hotelling observer computation.Med Phys. 2018 Jul;45(7):3019-3030. doi: 10.1002/mp.12940. Epub 2018 May 17. Med Phys. 2018. PMID: 29704868 Free PMC article.
-
Task Equivalence for Model and Human-Observer Comparisons in SPECT Localization Studies.IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2016 Jun;63(3):1426-1434. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2016.2542042. Epub 2016 May 19. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2016. PMID: 27980345 Free PMC article.
-
Deep-learning model observer for a low-contrast hepatic metastases localization task in computed tomography.Med Phys. 2022 Jan;49(1):70-83. doi: 10.1002/mp.15362. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Med Phys. 2022. PMID: 34792800 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Search Strategies for Microcalcifications and Masses in 3D Images.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2018 Feb;10577:105770C. doi: 10.1117/12.2293871. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2018. PMID: 32435079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wells R. G., King M. A., Gifford H. C., and Pretorius P. H., “Single-slice versus multi-slice display for human-observer lesion-detection studies,” IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 47, 1037–1044 (2000).10.1109/23.856544 - DOI
-
- Chen M., Bowsher J., Baydush A. H., Gilland K. L., DeLong D. M., and Jaszczak R. J., “Using the Hotelling observer on multislice and multiview simulated SPECT myocardial images,” IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 49, 661–667 (2002).10.1109/TNS.2002.1039546 - DOI
-
- Kim J., Kinahan P., Lartizien C., Comtat C., and Lewellen T. K., “A comparison of planar versus volumetric numerical observers for detection task performance in whole-body PET imaging,” IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 51, 34–40 (2004).10.1109/TNS.2004.823329 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

