Semiautomatic regional segmentation to measure orbital fat volumes in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy. A validation study
- PMID: 24007725
- PMCID: PMC4202813
- DOI: 10.1177/197140091302600402
Semiautomatic regional segmentation to measure orbital fat volumes in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy. A validation study
Abstract
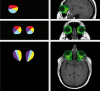
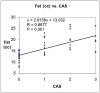
This study was designed to validate a novel semi-automated segmentation method to measure regional intra-orbital fat tissue volume in Graves' ophthalmopathy. Twenty-four orbits from 12 patients with Graves' ophthalmopathy, 24 orbits from 12 controls, ten orbits from five MRI study simulations and two orbits from a digital model were used. Following manual region of interest definition of the orbital volumes performed by two operators with different levels of expertise, an automated procedure calculated intra-orbital fat tissue volumes (global and regional, with automated definition of four quadrants). In patients with Graves' disease, clinical activity score and degree of exophthalmos were measured and correlated with intra-orbital fat volumes. Operator performance was evaluated and statistical analysis of the measurements was performed. Accurate intra-orbital fat volume measurements were obtained with coefficients of variation below 5%. The mean operator difference in total fat volume measurements was 0.56%. Patients had significantly higher intra-orbital fat volumes than controls (p<0.001 using Student's t test). Fat volumes and clinical score were significantly correlated (p<0.001). The semi-automated method described here can provide accurate, reproducible intra-orbital fat measurements with low inter-operator variation and good correlation with clinical data.
Figures

References
-
- Tian S, Nishida Y, Isberg B, et al. MRI measurements of normal extra ocular muscles and other orbital structures. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2000;238:393–404. - PubMed
-
- Feldon SE, Celina P, Saundra K, et al. Quantitive computer tomography of Graves' ophthalmopathy. Arch Ophtal. 1985;103:213–215. - PubMed
-
- Peyster RG, Ginsberg F, Silber JH, et al. Exophthalmos caused by excessive fat: CT volumetric analysis and differential diagnosis. Am J Roentgenol. 1986;146:459–464. - PubMed
-
- Nishida Y, Aoki Y, Hayashi O, et al. Volume measurement of horizontal extra ocular muscles with magnetic resonance imaging. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 1996;40:439–446. - PubMed
-
- Majos A, Grzelak P, Mynarczyk W, et al. Assessment of the volume of intra-orbital structures using the numerical segmentation image technique (NSI): the extra ocular muscles. Endokrynol Pol. 2007;58(2):110–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

