Endocannabinoid crosstalk between placenta and maternal fat in a baboon model (Papio spp.) of obesity
- PMID: 24008071
- PMCID: PMC3827983
- DOI: 10.1016/j.placenta.2013.08.007
Endocannabinoid crosstalk between placenta and maternal fat in a baboon model (Papio spp.) of obesity
Abstract
Introduction: Maternal obesity (MO) remains a serious obstetric problem with acute and chronic morbidities for both mothers and offspring. The mechanisms underlying these adverse consequences of MO remain unknown. Endocannabinoids (ECB) are neuromodulatory lipids released from adipocytes and other tissues. Metabolic crosstalk between placenta and adipocytes may mediate sequelae of MO. The goal of this study was to elucidate placental and systemic ECB in MO.
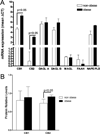
Material and methods: Placentas, sera, and subcutaneous fat were collected at Cesarean sections performed near term (0.9 G) in four non-obese (nOB) and four obese (OB) baboons (Papio spp.). Concentrations of anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) were measured by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. AEA and 2-AG pathways were characterized in placentas by Q-RT-PCR, Western blot and immunohistochemistry.
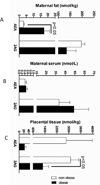
Results: Placental 2-AG levels were lower and maternal fat AEA levels were higher in OB (1254.1 ± 401.3 nmol/kg and 17.3 ± 4 nmol/kg) vs. nOB (3124.2 ± 557.3 nmol/kg and 3.1 ± 0.6 nmol/kg) animals. Concentrations of 2-AG correlated positively between maternal fat and placenta (r = 0.82, p = 0.013), but correlated negatively with maternal leptin concentrations (r = -0.72, p = 0.04 and r = -0.83, p = 0.01, respectively).
Conclusion: This is the first study to demonstrate differential ECB pathway regulation in maternal fat and placenta in MO. Differential regulation and function exist for AEA and 2-AG as the major ECB pathways in placenta.
Keywords: Endocannabinoids; Fat; Maternal obesity; Placenta.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
References
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. JAMA. 2010 Jan 20;303(3):235–241. PubMed PMID: 20071471. Epub 2010/01/15. eng. - PubMed
-
- Guelinckx I, Devlieger R, Beckers K, Vansant G. Maternal obesity: pregnancy complications, gestational weight gain and nutrition. Obes Rev. 2008 Mar;9(2):140–150. PubMed PMID, 18221480. Epub 2008/01/29. eng. - PubMed
-
- Bellocchio L, Cervino C, Pasquali R, Pagotto U. The endocannabinoid system and energy metabolism. J Neuroendocrinol. 2008 Jun;20(6):850–857. PubMed PMID, 18601709. Epub 2008/07/08. eng. - PubMed
-
- Bermudez-Silva FJ, Cardinal P, Cota D. The role of the endocannabinoid system in the neuroendocrine regulation of energy balance. J Psychopharmacol. 2012 Jan;26(1):114–124. PubMed PMID, 21824982. Epub 2011/08/10. eng. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous