Diagnostic work-up and surgery in participants of the Gdansk lung cancer screening programme: the incidence of surgery for non-malignant conditions
- PMID: 24008181
- PMCID: PMC3829503
- DOI: 10.1093/icvts/ivt388
Diagnostic work-up and surgery in participants of the Gdansk lung cancer screening programme: the incidence of surgery for non-malignant conditions
Abstract
Objectives: Low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) screening improves lung cancer prognosis but also results in diagnostic work-up and surgical treatment in many individuals without cancer. Therefore, we analysed the procedures that screening participants underwent to better understand the extent of overdiagnosis.
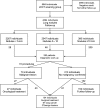
Methods: Between 2009 and 2011, 8649 healthy volunteers aged 50-75 years with a 20 pack-year smoking history underwent LDCT screening, of whom individuals with detected lung nodules had 2 years control. Participants with a nodule >10 mm in diameter or with suspected tumour morphology underwent diagnostic work-up: 283 (6%)/4694 (54%) screened participants had detected lung nodules. One hundred and four individuals underwent surgery, 27 underwent oncological treatment and 152 without a cancer diagnosis underwent further follow-up with LDCT.
Results: In 75% of participants accepted for diagnostic work-up and 25% of surgical patients, the procedures were unnecessary. In 70 (24.7%) participants, a specific diagnosis was obtained mainly due to the low efficacy of fine needle aspiration biopsy [sensitivity, 65.2%; negative predictive value (NPV), 95.9%] and bronchofiberoscopy (sensitivity, 71.4%; NPV, 50%) caused by overinterpretation of LDCT [positive predictive value (PPV), 2%]. Of 104 (36.7%) surgical patients, 43 (41.4%) had a preoperative cancer diagnosis, and 61 (58.6%) underwent surgery without pathological examination. In the latter group, intervention was justified in 35 (57.3%) patients. Complications occurred in 49 (17.3%) participants subjected to diagnostic work-up. In surgical patients, 67 (64.4%) malignant and 37 (35.6%) benign lesions were resected. In the latter group, intervention was justified in only 11 (29.7%) patients. No patient died because of diagnostic or treatment procedures during the study. The complication rate was 14.5% in the malignant and 10.8% in the benign groups. A neoplasm was found in 94 screening participants, of whom 67 (71.3%) underwent surgery; the remaining 27 (28.7%) patients were not surgical candidates. Adenocarcinoma accounted for 49/67 (73%) patients who underwent surgery for non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC); 56/67 (84%) patients had stage I NSCLC, and 26/67 (38%) underwent video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery lobectomy.
Conclusions: Futile diagnostic work-ups and operations must be reduced before LDCT screening can be broadly used. Stage I adenocarcinoma dominated in the NSCLC patients who underwent surgery.
Keywords: Early detection; Low-dose computed tomography; Lung cancer; Screening; Surgery.
Figures
Comment in
-
eComment. Positron emission tomography reduces the incidence of surgery for non-malignant conditions in lung cancer screening programmes.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2013 Dec;17(6):973. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivt458. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2013. PMID: 24243944 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Low-dose CT screening among never-smokers with or without a family history of lung cancer in Taiwan: a prospective cohort study.Lancet Respir Med. 2024 Feb;12(2):141-152. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00338-7. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Lancet Respir Med. 2024. PMID: 38042167
-
Can lung cancer screening by computed tomography be effective in areas with endemic histoplasmosis?J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011 Mar;141(3):688-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2010.08.045. Epub 2010 Oct 8. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011. PMID: 20933243
-
Lung cancer screening with low dose CT: experience at Campus Bio-Medico of Rome on 1500 patients.Minerva Chir. 2015 Dec;70(6):393-9. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Minerva Chir. 2015. PMID: 25700151
-
Video-assisted thoracoscopic solitary pulmonary nodule resection after CT-guided hookwire localization: 43 cases report and literature review.Surg Endosc. 2011 Jun;25(6):1723-9. doi: 10.1007/s00464-010-1502-3. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Surg Endosc. 2011. PMID: 21181200 Review.
-
Multidisciplinary management of the solitary pulmonary nodule (SPN): our opinion.Radiol Med. 2005 Sep;110(3):149-55. Radiol Med. 2005. PMID: 16200037 Review. English, Italian. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Futile lobectomies following video-thoracoscopic exploration for indeterminate pulmonary nodules: a retrospective study.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Aug;14(8):2826-2834. doi: 10.21037/jtd-21-1789. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 36071782 Free PMC article.
-
Incidentally diagnosed pulmonary nodule: a diagnostic algorithm.Kardiochir Torakochirurgia Pol. 2014 Dec;11(4):397-403. doi: 10.5114/kitp.2014.47339. Epub 2014 Nov 30. Kardiochir Torakochirurgia Pol. 2014. PMID: 26336456 Free PMC article.
-
Recommendations from the European Society of Thoracic Surgeons (ESTS) regarding computed tomography screening for lung cancer in Europe.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2017 Mar 1;51(3):411-420. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezw418. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2017. PMID: 28137752 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of thoracoscopic anatomical segmentectomy for small pulmonary nodules.World J Clin Cases. 2020 Jun 6;8(11):2227-2234. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i11.2227. World J Clin Cases. 2020. PMID: 32548153 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Exosomes and Their miRNA Load-A Potential Biomarker of Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 18;13(6):1373. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061373. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803617 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Henschke CI, Yankelevitz DF, Libby DM, Pasmantier MW, Smith JP, Miettinen OS. Survival of patients with stage I lung cancer detected on CT screening. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1763–71. - PubMed
-
- Van't Westeinde SC, van Klaveren RJ. Screening and early detection of lung cancer. Cancer J. 2011;17:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Frame PS. Routine screening for lung cancer?: Maybe someday, but not yet. JAMA. 2000;284:1980–3. - PubMed
-
- Bach PB, Jett JR, Pastorino U, Tockman MS, Swensen SJ, Begg CB. Computed tomography screening and lung cancer outcomes. JAMA. 2007;297:953–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical