Effects of high glucose-induced Cx43 downregulation on occludin and ZO-1 expression and tight junction barrier function in retinal endothelial cells
- PMID: 24008412
- PMCID: PMC3790390
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.13-11763
Effects of high glucose-induced Cx43 downregulation on occludin and ZO-1 expression and tight junction barrier function in retinal endothelial cells
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate whether high glucose (HG)-induced downregulation of connexin 43 (Cx43), a gap junction protein, alters ZO-1 and occludin expression and cell monolayer permeability.
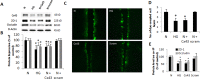
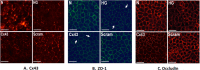
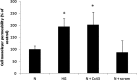
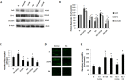
Methods: Rat retinal endothelial cells (RRECs) were grown in normal (N; 5 mM) medium, high glucose (HG; 30 mM) medium, N medium transfected with Cx43 siRNA, or N medium transfected with scrambled siRNA. To determine Cx43, occludin, and ZO-1 protein expression, Western blot (WB) analysis and immunostaining were performed. Gap junction intercellular communication (GJIC) was determined using scrape load dye transfer (SLDT) assay. In parallel, cell monolayer permeability was assessed in the four groups of cells, and in cells transfected with Cx43 plasmid or dominant negative Cx43 plasmid.
Results: Connexin 43 protein expression was significantly reduced in cells grown in HG (67 ± 15% of control), and a significant reduction in Cx43 was achieved when cells grown in N medium were transfected with Cx43 siRNA (76 ± 12% of control), with concomitant decrease in GJIC activity. Cells grown in HG showed significant reduction in occludin (77 ± 9% of control) and ZO-1 (80 ± 11% of control) protein level compared with cells grown in N media. Importantly, cells transfected with Cx43 siRNA and grown in N medium showed significant downregulation in occludin (78 ± 8% of control) and ZO-1 (81 ± 6% of control) expression, and exhibited increased cell monolayer permeability. Furthermore, Cx43 upregulation protected cells against HG-induced excess cell monolayer permeability.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that HG-induced downregulation of Cx43 expression and GJIC may contribute to the breakdown of endothelial barrier tight junctions associated with diabetic retinopathy.
Keywords: connexins; gap junctions; tight junctions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High glucose alters Cx43 expression and gap junction intercellular communication in retinal Müller cells: promotes Müller cell and pericyte apoptosis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Jun 17;55(7):4327-37. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-14606. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24938518 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of connexin 43 expression by high glucose reduces gap junction activity in microvascular endothelial cells.Diabetes. 2002 May;51(5):1565-71. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.5.1565. Diabetes. 2002. PMID: 11978657
-
High glucose-induced downregulation of connexin 30.2 promotes retinal vascular lesions: implications for diabetic retinopathy.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Mar 28;54(3):2361-6. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-10815. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23385797 Free PMC article.
-
Association of reduced Connexin 43 expression with retinal vascular lesions in human diabetic retinopathy.Exp Eye Res. 2016 May;146:103-106. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.12.011. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Exp Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26738943 Review.
-
Cx43 and the Actin Cytoskeleton: Novel Roles and Implications for Cell-Cell Junction-Based Barrier Function Regulation.Biomolecules. 2020 Dec 10;10(12):1656. doi: 10.3390/biom10121656. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33321985 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Benzalkonium chloride suppresses rabbit corneal endothelium intercellular gap junction communication.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 9;9(10):e109708. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109708. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25299343 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial effects of fenofibric acid on overexpression of extracellular matrix components, COX-2, and impairment of endothelial permeability associated with diabetic retinopathy.Exp Eye Res. 2015 Nov;140:124-129. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.08.010. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Exp Eye Res. 2015. PMID: 26297615 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine mediated monocyte trafficking into the retina: role of inflammation in alteration of the blood-retinal barrier in diabetic retinopathy.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 20;9(10):e108508. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108508. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25329075 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Connexin in Ophthalmic Neovascularization and the Interaction between Connexin and Proangiogenic Factors.J Ophthalmol. 2022 Jun 22;2022:8105229. doi: 10.1155/2022/8105229. eCollection 2022. J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35783340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COMP-Ang1 Stabilizes Hyperglycemic Disruption of Blood-Retinal Barrier Phenotype in Human Retinal Microvascular Endothelial Cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019 Aug 1;60(10):3547-3555. doi: 10.1167/iovs.19-27644. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019. PMID: 31415078 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antonetti DA, Barber AJ, Khin S, Lieth E, Tarbell JM, Gardner TW. Vascular permeability in experimental diabetes is associated with reduced endothelial occludin content: vascular endothelial growth factor decreases occludin in retinal endothelial cells. Penn State Retina Research Group. Diabetes. 1998; 47: 1953– 1959 - PubMed
-
- Rincon-Choles H, Vasylyeva TL, Pergola PE, et al. ZO-1 expression and phosphorylation in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 2006; 55: 894– 900 - PubMed
-
- Lang GE. Diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmologica. 2012; 227 (suppl 1): 21– 29 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

