Members of the EpCAM signalling pathway are expressed in gastric cancer tissue and are correlated with patient prognosis
- PMID: 24008668
- PMCID: PMC3798952
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2013.536
Members of the EpCAM signalling pathway are expressed in gastric cancer tissue and are correlated with patient prognosis
Abstract
Background: We investigated the expression of members of the epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) signalling pathway in gastric cancer (GC) testing the following hypotheses: are these molecules expressed in GC and are they putatively involved in GC biology.
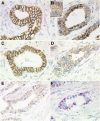
Methods: The study cohort consisted of 482 patients. The following members of the EpCAM signalling pathway were analysed by immunohistochemistry and were correlated with various clinico-pathological patient characteristics: extracellular domain of EpCAM (EpEX), intracellular domain of EpCAM (EpICD), E-cadherin, β-catenin, presenilin-2 (PSEN2), and ADAM17.
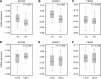
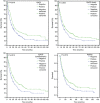
Results: All members of the EpCAM signalling pathway were differentially expressed in GC. The expression correlated significantly with tumour type (EpEX, EpICD, E-cadherin, β-catenin, and PSEN2), mucin phenotype (EpEX, EpICD, β-catenin, and ADAM17), T-category (EpEX, E-cadherin, and β-catenin), N-category (EpEX and β-catenin), UICC tumour stage (EpEX, EpICD, β-catenin, and PSEN2), tumour grade (EpEX, EpICD, E-cadherin, β-catenin, and PSEN2), and patients' survival (EpEX, EpICD, and PSEN2). A significant coincidental expression in GC was found for EpEX, EpICD, E-cadherin, β-catenin, PSEN2, and ADAM17. Decreased immunodetection of EpEX in locally advanced GC was not associated with decreased EpCAM mRNA levels.
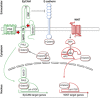
Conclusion: All members of the EpCAM signalling pathway are expressed in GC. The expression correlated significantly with each other and with various clinico-pathological patient characteristics, including patients' survival. Thus, the EpCAM signalling pathway is a highly interesting putative therapeutic target in GC.
Figures

References
-
- Alberts SR, Cervantes A, van de Velde CJ. Gastric cancer: epidemiology, pathology and treatment. Ann Oncol. 2003;14 (Suppl 2:ii31–ii36. - PubMed
-
- Brunkan AL, Goate AM. Presenilin function and gamma-secretase activity. J Neurochem. 2005;93 (4:769–792. - PubMed
-
- Buhard O, Cattaneo F, Wong YF, Yim SF, Friedman E, Flejou JF, Duval A, Hamelin R. Multipopulation analysis of polymorphisms in five mononucleotide repeats used to determine the microsatellite instability status of human tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24 (2:241–251. - PubMed
-
- Campbell WA, Iskandar MK, Reed ML, Xia W. Endoproteolysis of presenilin in vitro: inhibition by gamma-secretase inhibitors. Biochemistry. 2002;41 (10:3372–3379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

