Repression of c-Kit by p53 is mediated by miR-34 and is associated with reduced chemoresistance, migration and stemness
- PMID: 24009080
- PMCID: PMC3824539
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.1202
Repression of c-Kit by p53 is mediated by miR-34 and is associated with reduced chemoresistance, migration and stemness
Abstract
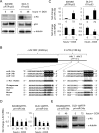
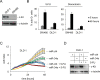
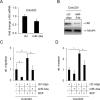
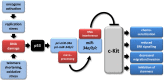
The c-Kit receptor tyrosine kinase is commonly over-expressed in different types of cancer. p53 activation is known to result in the down-regulation of c-Kit. However, the underlying mechanism has remained unknown. Here, we show that the p53-induced miR-34 microRNA family mediates repression of c-Kit by p53 via a conserved seed-matching sequence in the c-Kit 3'-UTR. Ectopic miR-34a resulted in a decrease in Erk signaling and transformation, which was dependent on the down-regulation of c-Kit expression. Furthermore, ectopic expression of c-Kit conferred resistance of colorectal cancer (CRC) cells to treatment with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), whereas ectopic miR-34a sensitized the cells to 5-FU. After stimulation with c-Kit ligand/stem cell factor (SCF) Colo320 CRC cells displayed increased migration/invasion, whereas ectopic miR-34a inhibited SCF-induced migration/invasion. Activation of a conditional c-Kit allele induced several stemness markers in DLD-1 CRC cells. In primary CRC samples elevated c-Kit expression also showed a positive correlation with markers of stemness, such as Lgr5, CD44, OLFM4, BMI-1 and β-catenin. On the contrary, activation of a conditional miR-34a allele in DLD-1 cells diminished the expression of c-Kit and several stemness markers (CD44, Lgr5 and BMI-1) and suppressed sphere formation. MiR-34a also suppressed enhanced sphere-formation after exposure to SCF. Taken together, our data establish c-Kit as a new direct target of miR-34 and demonstrate that this regulation interferes with several c-Kit-mediated effects on cancer cells. Therefore, this regulation may be potentially relevant for future diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MiR-148a suppressed cell invasion and migration via targeting WNT10b and modulating β-catenin signaling in cisplatin-resistant colorectal cancer cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jan;109:902-909. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.080. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30551544
-
Characterization of a p53/miR-34a/CSF1R/STAT3 Feedback Loop in Colorectal Cancer.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;10(2):391-418. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2020.04.002. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32304779 Free PMC article.
-
SNAIL and miR-34a feed-forward regulation of ZNF281/ZBP99 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition.EMBO J. 2013 Nov 27;32(23):3079-95. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.236. Epub 2013 Nov 1. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 24185900 Free PMC article.
-
ZNF281/ZBP-99: a new player in epithelial-mesenchymal transition, stemness, and cancer.J Mol Med (Berl). 2014 Jun;92(6):571-81. doi: 10.1007/s00109-014-1160-3. Epub 2014 May 18. J Mol Med (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24838609 Review.
-
miR-34: from bench to bedside.Oncotarget. 2014 Feb 28;5(4):872-81. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1825. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24657911 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting miR-34a/Pdgfra interactions partially corrects alveologenesis in experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia.EMBO Mol Med. 2019 Mar;11(3):e9448. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201809448. EMBO Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30770339 Free PMC article.
-
Role of miR-34a as a suppressor of L1CAM in endometrial carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2014 Jan 30;5(2):462-72. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1552. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24497324 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC 1/4-mediated silencing of microRNA-200b promotes chemoresistance in human lung adenocarcinoma cells.Oncotarget. 2014 May 30;5(10):3333-49. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1948. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 24830600 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of p53-inducible long non-coding RNA LINC01021 increases chemosensitivity.Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 1;8(61):102783-102800. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22245. eCollection 2017 Nov 28. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29262524 Free PMC article.
-
miR-497 and miR-34a retard lung cancer growth by co-inhibiting cyclin E1 (CCNE1).Oncotarget. 2015 May 30;6(15):13149-63. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3693. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25909221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Besmer P, Murphy JE, George PC, Qiu FH, Bergold PJ, Lederman L, Snyder HW, Jr, Brodeur D, Zuckerman EE, Hardy WD. A new acute transforming feline retrovirus and relationship of its oncogene v-kit with the protein kinase gene family. Nature. 1986;320(6061):415–421. - PubMed
-
- Anderson DM, Lyman SD, Baird A, Wignall JM, Eisenman J, Rauch C, March CJ, Boswell HS, Gimpel SD, Cosman D, et al. Molecular cloning of mast cell growth factor, a hematopoietin that is active in both membrane bound and soluble forms. Cell. 1990;63(1):235–243. - PubMed
-
- Lennartsson J, Ronnstrand L. Stem Cell Factor Receptor/c-Kit: From Basic Science to Clinical Implications. Physiol Rev. 2012;92(4):1619–1649. - PubMed
-
- Rothschild G, Sottas CM, Kissel H, Agosti V, Manova K, Hardy MP, Besmer P. A role for kit receptor signaling in Leydig cell steroidogenesis. Biol Reprod. 2003;69(3):925–932. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

