Renal outcomes and clinical course of nondiabetic renal diseases in patients with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 24009452
- PMCID: PMC3759762
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2013.28.5.565
Renal outcomes and clinical course of nondiabetic renal diseases in patients with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Background/aims: In several recent studies, renal biopsies in patients with type 2 diabetes and renal disease have revealed a heterogeneous group of disease entities. Our aim was to study the prognosis and clinical course of nondiabetic renal disease (NDRD) and to determine risk factors for NDRD in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods: Renal biopsy reports of 110 patients with type 2 diabetes who were seen at Kyung Hee University Medical Center and Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea between January 2000 and December 2011 were retrospectively analyzed.
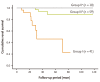
Results: Of 110 patients with type 2 diabetes, 41 (37.3%) had diabetic nephropathy (DN), 59 (53.6%) had NDRD, and 10 (9.1%) had NDRD superimposed on DN. Immunoglobulin A nephropathy (43.5%) was the most common NDRD. Patients with NDRD had a shorter duration of diabetes, lower frequency of diabetic retinopathy, and better renal outcomes, which might have resulted from the use of aggressive disease-specific treatments such as steroids and immunosuppressants in patients with NDRD.
Conclusions: Compared with DN, NDRD was associated with better renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes, as evidenced by a higher cumulative renal survival rate and lower rate of end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Shorter duration of diabetes and absence of retinopathy were independent predictors of NDRD in patients with type 2 diabetes and renal involvement. Renal biopsy is recommended for patients with type 2 diabetes and risk factors for NDRD, to obtain an accurate diagnosis, prompt initiation of disease-specific treatment, and ultimately better renal outcomes with the avoidance of ESRD.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus, type 2; Diabetic nephropathies; Non-diabetic renal disease.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article is reported.
Figures
Comment in
-
Does nondiabetic renal disease exacerbate diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes?Korean J Intern Med. 2013 Sep;28(5):544-6. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2013.28.5.544. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Korean J Intern Med. 2013. PMID: 24009449 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kikkawa R, Koya D, Haneda M. Progression of diabetic nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;41(3 Suppl 1):S19–S21. - PubMed
-
- Pham TT, Sim JJ, Kujubu DA, Liu IL, Kumar VA. Prevalence of nondiabetic renal disease in diabetic patients. Am J Nephrol. 2007;27:322–328. - PubMed
-
- Lee HB, Seo JY, Yu MR, Uh ST, Ha H. Radical approach to diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int Suppl. 2007;(106):S67–S70. - PubMed
-
- Mather HM, Chaturvedi N, Kehely AM. Comparison of prevalence and risk factors for microalbuminuria in South Asians and Europeans with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 1998;15:672–677. - PubMed
-
- Earle KA, Mehrotra S, Dalton RN, Denver E, Swaminathan R. Defective nitric oxide production and functional renal reserve in patients with type 2 diabetes who have microalbuminuria of African and Asian compared with white origin. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12:2125–2130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
