Adenine Dinucleotide Second Messengers and T-lymphocyte Calcium Signaling
- PMID: 24009611
- PMCID: PMC3756424
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00259
Adenine Dinucleotide Second Messengers and T-lymphocyte Calcium Signaling
Abstract
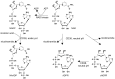
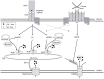
Calcium signaling is a universal signal transduction mechanism in animal and plant cells. In mammalian T-lymphocytes calcium signaling is essential for activation and re-activation and thus important for a functional immune response. Since many years it has been known that both calcium release from intracellular stores and calcium entry via plasma membrane calcium channels are involved in shaping spatio-temporal calcium signals. Second messengers derived from the adenine dinucleotides NAD and NADP have been implicated in T cell calcium signaling. Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) acts as a very early second messenger upon T cell receptor/CD3 engagement, while cyclic ADP-ribose (cADPR) is mainly involved in sustained partial depletion of the endoplasmic reticulum by stimulating calcium release via ryanodine receptors. Finally, adenosine diphosphoribose (ADPR) a breakdown product of both NAD and cADPR activates a plasma membrane cation channel termed TRPM2 thereby facilitating calcium (and sodium) entry into T cells. Receptor-mediated formation, metabolism, and mode of action of these novel second messengers in T-lymphocytes will be reviewed.
Keywords: T-lymphocyte; TRPM2 cation channels; adenosine diphosphoribose; calcium entry; calcium release; calcium signaling; cyclic ADP-ribose; nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of calcium signalling by adenine-based second messengers.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Feb;35(Pt 1):109-14. doi: 10.1042/BST0350109. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 17233614 Review.
-
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate and cyclic ADP-ribose regulate TRPM2 channels in T lymphocytes.FASEB J. 2006 May;20(7):962-4. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-5538fje. Epub 2006 Apr 3. FASEB J. 2006. PMID: 16585058
-
Adenine nucleotide diphosphates: emerging second messengers acting via intracellular Ca2+ release.Am J Physiol. 1996 Oct;271(4 Pt 1):C1007-24. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1996.271.4.C1007. Am J Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8897805 Review.
-
Identification of direct and indirect effectors of the transient receptor potential melastatin 2 (TRPM2) cation channel.J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 24;285(39):30091-102. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.066464. Epub 2010 Jul 22. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20650899 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of calcium signaling by the second messenger cyclic adenosine diphosphoribose (cADPR).Curr Mol Med. 2004 May;4(3):239-48. doi: 10.2174/1566524043360771. Curr Mol Med. 2004. PMID: 15101682 Review.
Cited by
-
CD38 is expressed on inflammatory cells of the intestine and promotes intestinal inflammation.PLoS One. 2015 May 4;10(5):e0126007. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126007. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25938500 Free PMC article.
-
NAD+ Metabolism and Interventions in Premature Renal Aging and Chronic Kidney Disease.Cells. 2022 Dec 21;12(1):21. doi: 10.3390/cells12010021. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36611814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ion channels in innate and adaptive immunity.Annu Rev Immunol. 2015;33:291-353. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112212. Annu Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25861976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD38 Expression in a Subset of Memory T Cells Is Independent of Cell Cycling as a Correlate of HIV Disease Progression.Dis Markers. 2016;2016:9510756. doi: 10.1155/2016/9510756. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Dis Markers. 2016. PMID: 27064238 Free PMC article.
-
The N-terminal domain in TRPM2 channel is a conserved nucleotide binding site.J Gen Physiol. 2020 May 4;152(5):e201912555. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201912555. J Gen Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32282890 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

