A giant peritoneal loose body
- PMID: 24009634
- PMCID: PMC3759638
- DOI: 10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.4.378
A giant peritoneal loose body
Abstract
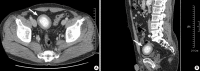
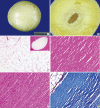
Peritoneal loose bodies (PLBs) are usually discovered incidentally during laparotomy or autopsy. A few cases of giant PLBs presenting with various symptoms have been reported in the literature. Here, we describe a case of a giant PLB incidentally found in the pelvic cavity of a 50-year-old man. Computed tomography revealed a free ovoid mass in the pelvic cavity that consisted of central dense, heterogeneous calcifications and peripheral soft tissue. The mass was an egg-shaped, hard, glistening concretion measuring 7.5×7.0×6.8 cm and weighing 160 g. This concretion consisted of central necrotic fatty tissue surrounded by concentrically laminated, acellular, fibrous material. Small PLBs usually do not require any specific treatment. However, if PLBs cause alimentary or urinary symptoms due to their large size, surgical removal may be recommended. It is essential for clinicians to be aware of this entity and its characteristic features to establish the correct diagnosis.
Keywords: Colon; Loose body; Peritoneum.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Desai HP, Tripodi J, Gold BM, Burakoff R. Infarction of an epiploic appendage: review of the literature. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1993;16:323–325. - PubMed
-
- Takada A, Moriya Y, Muramatsu Y, Sagae T. A case of giant peritoneal loose bodies mimicking calcified leiomyoma originating from the rectum. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1998;28:441–442. - PubMed
-
- Takabe K, Greenberg JI, Blair SL. Giant peritoneal loose bodies. J Gastrointest Surg. 2006;10:465–468. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh P, Strong C, Naugler W, Haghighi P, Carethers JM. Peritoneal mice implicated in intestinal obstruction: report of a case and review of the literature. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2006;40:427–430. - PubMed
-
- Bhandarwar AH, Desai VV, Gajbhiye RN, Deshraj BP. Acute retention of urine due to a loose peritoneal body. Br J Urol. 1996;78:951–952. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

