Preliminary experience in the management of tracheobronchial foreign bodies in Lagos, Nigeria
- PMID: 24009807
- PMCID: PMC3758847
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2013.15.31.2710
Preliminary experience in the management of tracheobronchial foreign bodies in Lagos, Nigeria
Abstract
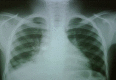
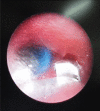
Aspiration of tracheobronchial foreign bodies commonly affects young children, is potentially life threatening and requires early intervention for extraction. Access to facilities and skill manpower for bronchoscopic extraction is however limited in Nigeria. The aim of this study is to describe the experience in our institution with bronchoscopic removal of tracheobronchial foreign bodies and highlight the challenges encountered. This is a retrospective study of all patients referred to the Lagos State University Teaching Hospital with a diagnosis of tracheobronchial foreign body within the period of February 2008 and February 2013. Data extracted from the medical records were age, sex, time interval between aspiration and presentation, location of tracheobronchial foreign body, bronchoscopic technique, complications and outcome. A total of 24 patients were referred and confirmed at bronchoscopy to have tracheobronchial foreign bodies. Mean age was 6.6 + 5 years. Male to female ratio was 1:1. Delayed presentation was common with 22 patients (91.7%) presenting more than 24 hours after aspiration. Aspirated material was inorganic in 17 patients (70.8%) and organic in 7 patients (29.2%). Location of tracheobronchial foreign bodies was right main bronchus in 16 patients (66.7%), left main bronchus in 6 patients (25%) and the trachea in 2 patients (8.3%). Challenges to speedy and safe removal of the foreign bodies were delayed presentation and a limited range of bronchoscopic equipment early in the series which caused prolonged procedures and increased complications. Two mortalities occurred early in the series; one from airway obstruction and the other from respiratory failure caused by tracheobronchial oedema. Extraction of tracheobronchial foreign bodies was faster, more complete and safer later in the series due to a wider range of bronchoscopy equipment which included both flexible and rigid videobronchoscopy with the use of optical forceps. This preliminary experience suggests that an adequate armamentarium of bronchoscopy equipment is required to increase the chances of complete extraction, speed up the procedure and reduce the risk of complications of Tracheobronchial Foreign Bodies in our environment. Delayed presentation increases the difficulty of the procedure so earlier referral of these patients would help reduce the risk involved in their management.
Keywords: Bronchoscopy; Lagos; Nigeria; Tracheobronchial Foreign Bodies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of flexible bronchoscopy accomplished through a laryngeal mask airway in the treatment of tracheobronchial foreign bodies in children.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Feb;117:194-197. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2018.12.006. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 30579081
-
[Experience in the removal of difficult and high risk tracheobronchial foreign body by bronchoscopy].Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012 Dec;47(12):982-6. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23328036 Chinese.
-
Diagnosis and treatment of tracheobronchial foreign bodies in 1024 children.J Pediatr Surg. 2012 Nov;47(11):2004-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2012.07.036. J Pediatr Surg. 2012. PMID: 23163990
-
Tracheobronchial aspiration of foreign bodies and rigid bronchoscopy in children.Pediatr Int. 2012 Aug;54(4):532-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200X.2012.03610.x. Epub 2012 May 30. Pediatr Int. 2012. PMID: 22414345 Review.
-
The anesthetic considerations of tracheobronchial foreign bodies in children: a literature review of 12,979 cases.Anesth Analg. 2010 Oct;111(4):1016-25. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181ef3e9c. Epub 2010 Aug 27. Anesth Analg. 2010. PMID: 20802055 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluate the Role of Rigid Bronchoscopy in Tracheo-Bronchial Foreign Bodies.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022 Dec;74(Suppl 3):5177-5181. doi: 10.1007/s12070-021-03053-2. Epub 2022 Feb 7. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022. PMID: 36742744 Free PMC article.
-
Death as a Consequence of Foreign Body Aspiration in Children.Med Arch. 2018 Jun;72(3):220-223. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2018.72.220-223. Med Arch. 2018. PMID: 30061771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Missed Distal Tracheal Foreign Body in Consecutive Bronchoscopies in a 6-year-old Boy.Niger J Surg. 2017 Jan-Jun;23(1):67-70. doi: 10.4103/1117-6806.199957. Niger J Surg. 2017. PMID: 28584516 Free PMC article.
-
The challenges of cardiothoracic surgery practice in Nigeria: a 12 years institutional experience.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2016 Oct;6(Suppl 1):S27-S43. doi: 10.21037/cdt.2016.09.05. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2016. PMID: 27904842 Free PMC article.
-
[Metallic foreign body inhalation: 36 months of intrabronchial evolution in an eight year-old child].Pan Afr Med J. 2014 Jul 17;18:225. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2014.18.225.4823. eCollection 2014. Pan Afr Med J. 2014. PMID: 25422700 Free PMC article. French.
References
-
- Orji FT, Akpeh JO. Tracheobronchial foreign body aspiration in children: how reliable are clinical and radiological signs in the diagnosis? Clin Otolaryngol. 2011;35(6):479–485. - PubMed
-
- Wang K, Harnden A, Thomson A. Easily missed? Foreign Body inhalation in children. Clinical Otolaryngology. 2010;35(6):494–495. - PubMed
-
- Onotai LO, Ebong ME. The pattern of foreign body impactions in the tracheobronchial tree in the University of Port Harcourt Teaching Hospital. Port Harcout Med J. 2011;5(2):130–135.
-
- Onotai LO, Ibekwe MU, George IO. Impacted foreign bodies in the larynx of Nigerian children. J Med Med Sci. 2012;3(4):217–221.
-
- Lima JA. Laryngeal foreign bodies in children: a persistent life threatening problem. The Laryngoscope. 1989;99(4):415–420. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical