Cementless total hip arthroplasty for patients with Crowe type III or IV developmental dysplasia of the hip: two-stage total hip arthroplasty following skeletal traction after soft tissue release for irreducible hips
- PMID: 24009901
- PMCID: PMC3758985
- DOI: 10.4055/cios.2013.5.3.167
Cementless total hip arthroplasty for patients with Crowe type III or IV developmental dysplasia of the hip: two-stage total hip arthroplasty following skeletal traction after soft tissue release for irreducible hips
Abstract
Background: Total hip arthroplasty (THA) for severe developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) is a technically demanding procedure for arthroplasty surgeons, and it is often difficult to reduce the hip joint without soft tissue release due to severe flexion contracture. We performed two-stage THAs in irreducible hips with expected lengthening of the affected limb after THA of over 2.5 cm or with flexion contractures of greater than 30 degrees in order to place the acetabular cup in the true acetabulum and to prevent neurologic deficits associated with acute elongation of the limb. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the outcomes of cementless THA in patients with severe DDH with a special focus on the results of two-stage THA.
Methods: Retrospective clinical and radiological evaluations were done on 17 patients with Crowe type III or IV developmental DDH treated by THA. There were 14 women and 3 men with a mean age of 52.3 years. Follow-ups averaged 52 months. Six cases were treated with two-stage THA followed by surgical hip liberalization and skeletal traction for 2 weeks.
Results: The mean Harris hip score improved from 40.9 to 89.1, and mean leg length discrepancy (LLD) in 13 unilateral cases was reduced from 2.95 to 0.8 cm. In the patients who underwent two-stage surgery, no nerve palsy was observed, and the single one-stage patient with incomplete peroneal nerve palsy recovered fully 4 weeks postoperatively.
Conclusions: The short-term clinical and radiographic outcomes of primary cementless THA for patients with Crowe type III or IV DDH were encouraging. Two-stage THA followed by skeletal traction after soft tissue release could provide alternative solutions to the minimization of limb shortenings or LLD without neurologic deficits in highly selected patients.
Keywords: Congenital hip dysplasia; Total hip arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
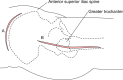
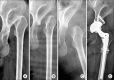
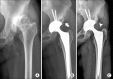
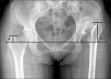

References
-
- Argenson JN, Flecher X, Parratte S, Aubaniac JM. Anatomy of the dysplastic hip and consequences for total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;465:40–45. - PubMed
-
- Crowe JF, Mani VJ, Ranawat CS. Total hip replacement in congenital dislocation and dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979;61(1):15–23. - PubMed
-
- Anwar MM, Sugano N, Masuhara K, Kadowaki T, Takaoka K, Ono K. Total hip arthroplasty in the neglected congenital dislocation of the hip: a five- to 14-year follow-up study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;(295):127–134. - PubMed
-
- Cameron HU, Botsford DJ, Park YS. Influence of the Crowe rating on the outcome of total hip arthroplasty in congenital hip dysplasia. J Arthroplasty. 1996;11(5):582–587. - PubMed
-
- Charnley J, Feagin JA. Low-friction arthroplasty in congenital subluxation of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1973;(91):98–113. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

