In silico screening of 393 mutants facilitates enzyme engineering of amidase activity in CalB
- PMID: 24010022
- PMCID: PMC3757469
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.145
In silico screening of 393 mutants facilitates enzyme engineering of amidase activity in CalB
Abstract
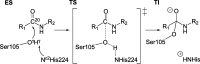
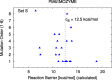
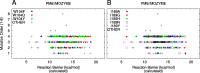
Our previously presented method for high throughput computational screening of mutant activity (Hediger et al., 2012) is benchmarked against experimentally measured amidase activity for 22 mutants of Candida antarctica lipase B (CalB). Using an appropriate cutoff criterion for the computed barriers, the qualitative activity of 15 out of 22 mutants is correctly predicted. The method identifies four of the six most active mutants with ≥3-fold wild type activity and seven out of the eight least active mutants with ≤0.5-fold wild type activity. The method is further used to screen all sterically possible (386) double-, triple- and quadruple-mutants constructed from the most active single mutants. Based on the benchmark test at least 20 new promising mutants are identified.
Keywords: Computational Chemistry; Enzyme Engineering.
Figures


References
-
- Fersht A. Enzyme structure and mechanism. W.H. Freeman and Company: CRC Press, Inc; 1985.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

