Genetic assemblage of Sarcocystis spp. in Malaysian snakes
- PMID: 24010903
- PMCID: PMC3847168
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-257
Genetic assemblage of Sarcocystis spp. in Malaysian snakes
Abstract
Background: Sarcocystis species are protozoan parasites with a wide host range including snakes. Although there were several reports of Sarcocytis species in snakes, their distribution and prevalence are still not fully explored.
Methods: In this study, fecal specimens of several snake species in Malaysia were examined for the presence of Sarcocystis by PCR of 18S rDNA sequence. Microscopy examination of the fecal specimens for sporocysts was not carried as it was difficult to determine the species of the infecting Sarcocystis.
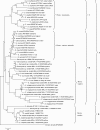
Results: Of the 28 snake fecal specimens, 7 were positive by PCR. BLASTn and phylogenetic analyses of the amplified 18S rDNA sequences revealed the snakes were infected with either S. nesbitti, S. singaporensis, S. zuoi or undefined Sarcocystis species.
Conclusion: This study is the first to report Sarcocystis infection in a cobra, and S. nesbitti in a reticulated python.
Figures
References
-
- Wong KT, Pathmanathan R. Human muscular sarcocystosis in Malaysia. Trop Geogr Med. 1993;45(4):191. - PubMed
-
- Sonnenburg F, Cramer J, Freedman D, Plier A, Esposito D, Sotir M, Lankau E. Notes from the field: acute muscular sarcocystosis among returning travelers-Tioman Island, Malaysia, 2011. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2012;61(2):37–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

