Nitrates and bone turnover (NABT) - trial to select the best nitrate preparation: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 24010992
- PMCID: PMC3847792
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-14-284
Nitrates and bone turnover (NABT) - trial to select the best nitrate preparation: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Organic nitrates uncouple bone turnover, improve bone mineral density, and improve trabecular and cortical components of bone. These changes in turnover, strength and geometry may translate into an important reduction in fractures. However, before proceeding with a large fracture trial, there is a need to identify the nitrate formulation that has both the greatest efficacy (with regards to bone turnover markers) and gives the fewest headaches. Ascertaining which nitrate formulation this may be is the purpose of the current study.
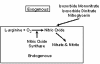
Methods and design: This will be an open-label randomized, controlled trial conducted at Women's College Hospital comparing five formulations of nitrates for their effects on bone turnover markers and headache. We will recruit postmenopausal women age 50 years or older with no contraindications to nitroglycerin. Our trial will consist of a run-in phase and a treatment phase. We will enroll 420 women in the run-in phase, each to receive all of the 5 potential treatments in random order for 2 days, each with a 2-day washout period between treatments. Those who tolerate all formulations will enter the 12-week treatment phase and be randomly assigned to one of five groups: 0.3 mg sublingual nitroglycerin tablet, 0.6 mg of the sublingual tablet, a 20 mg tablet of isosorbide mononitrate, a 160 mg nitroglycerin transdermal patch (used for 8 h), and 15 mg of nitroglycerin ointment as used in a previous trial by our group. We will continue enrolment until we have randomized 210 women or 35 women per group. Concentrations of bone formation (bone-specific alkaline phosphatase and procollagen type I N-terminal propeptide) and bone resorption (C-telopeptides of collagen crosslinks and N-terminal crosslinks of collagen) agents will be measured in samples taken at study entry (the start of the run in phase) and 12 weeks. Subjects will record the frequency and severity of headaches daily during the run-in phase and then monthly after that. We will use the 'multiple comparisons with the best' approach for data analyses, as this strategy allows practical considerations of ease of use and tolerability to guide selection of the preparation for future studies.
Discussion: Data from this protocol will be used to develop a randomized, controlled trial of nitrates to prevent osteoporotic fractures.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01387672. Controlled-Trials.com: ISRCTN08860742.
Figures
References
-
- Cummings SR, Kelsey JL, Nevitt MC, O’Dowd KJ. Epidemiology of osteoporosis and osteoporotic fracture. Epidemiol Rev. 1985;7:178–208. - PubMed
-
- Hawker G. In: Patterns of Health Care in Ontario: Arthritis and Related Conditions. Badley EM, Williams JI, editor. Toronto, Canada: Institute of Clinical Evaluative Sciences; 1998. Chapter 1: Epidemiology of arthritis and osteoporosis.
-
- Jaglal S. In: Patterns of Health Care in Ontario: Arthritis and Related Conditions. Bradley EM, Williams JI, editor. Toronto, Canada: Institute of Clinical Evaluative Sciences; 1998. Chapter 8: osteoporotic fractures: incidence and impact.
-
- Melton LJI, Cooper C. In: Osteoporosis. 2. Marcus R, Feldman D, Kelsey J, editor. Vol. 1. San Diego CA: Academic Press; 2001. Magnitude and impact of osteoporosis and fractures; pp. 557–567.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical