Targeting the PI3-kinase/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
- PMID: 24012393
- PMCID: PMC3811932
- DOI: 10.1016/j.soc.2013.06.008
Targeting the PI3-kinase/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
Abstract
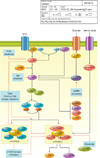
This article presents an overview of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. As a central regulator of cell growth, protein translation, survival, and metabolism, activation of this signaling pathway contributes to the pathogenesis of many tumor types. Biochemical and genetic aberrations of this pathway observed in various cancer types are explored. Last, pathway inhibitors both in development and already approved by the Food and Drug Administration are discussed.
Keywords: Cell signaling; Molecular targeted therapy; PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway; PTEN.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Vivanco I, Sawyers CL. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:489–501. - PubMed
-
- Guertin DA, Sabatini DM. Defining the role of mTOR in cancer. Cancer Cell. 2007;12:9–22. - PubMed
-
- Brugge J, Hung MC, Mills GB. A new mutational aktivation in the PI3K pathway. Cancer Cell. 2007;12:104–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

