Antihypertensive drug Valsartan promotes dendritic spine density by altering AMPA receptor trafficking
- PMID: 24012668
- PMCID: PMC3840727
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.08.091
Antihypertensive drug Valsartan promotes dendritic spine density by altering AMPA receptor trafficking
Abstract
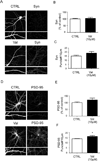
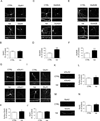
Recent studies demonstrated that the antihypertensive drug Valsartan improved spatial and episodic memory in mouse models of Alzheimer's Disease (AD) and human subjects with hypertension. However, the molecular mechanism by which Valsartan can regulate cognitive function is still unknown. Here, we investigated the effect of Valsartan on dendritic spine formation in primary hippocampal neurons, which is correlated with learning and memory. Interestingly, we found that Valsartan promotes spinogenesis in developing and mature neurons. In addition, we found that Valsartan increases the puncta number of PSD-95 and trends toward an increase in the puncta number of synaptophysin. Moreover, Valsartan increased the cell surface levels of AMPA receptors and selectively altered the levels of spinogenesis-related proteins, including CaMKIIα and phospho-CDK5. These data suggest that Valsartan may promote spinogenesis by enhancing AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity signaling.
Keywords: AMPA receptor; CaMKIIα; Spinogenesis; Valsartan.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Koyanagi R, Hagiwara N, Yamaguchi JI, Kawada-Watanabe E, Haruta S, Takagi A, Ogawa H. Efficacy of the combination of amlodipine and candesartan in hypertensive patients with coronary artery disease: A subanalysis of the HIJ-CREATE study. J Cardiol. 2013 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

