Tracking immune cells in vivo using magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 24013185
- PMCID: PMC3886235
- DOI: 10.1038/nri3531
Tracking immune cells in vivo using magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
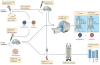
The increasing complexity of in vivo imaging technologies, coupled with the development of cell therapies, has fuelled a revolution in immune cell tracking in vivo. Powerful magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) methods are now being developed that use iron oxide- and ¹⁹F-based probes. These MRI technologies can be used for image-guided immune cell delivery and for the visualization of immune cell homing and engraftment, inflammation, cell physiology and gene expression. MRI-based cell tracking is now also being applied to evaluate therapeutics that modulate endogenous immune cell recruitment and to monitor emerging cellular immunotherapies. These recent uses show that MRI has the potential to be developed in many applications to follow the fate of immune cells in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare
Figures


References
-
- Bousso P, Moreau HD. Functional immunoimaging: the revolution continues. Nature Rev Immunol. 2012;12:858–864. - PubMed
-
- Thakur ML, Lavender JP, Arnot RN, Silvester DJ, Segal AW. Indium-111-labeled autologous leukocytes in man. J Nuclear Med. 1977;18:1014–1021. - PubMed
-
- Tjuvajev JG, et al. Imaging the expression of transfected genes in vivo. Cancer Res. 1995;55:6126–6132. - PubMed
-
- Koehne G, et al. Serial in vivo imaging of the targeted migration of human HSV-TK-transduced antigen-specific lymphocytes. Nature Biotech. 2003;21:405–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S10 OD010744/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01‑CA134633/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01‑DA026299/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB017271/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA134633/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA151838/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS045062/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB007825/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA026299/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U54‑CA151838/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01‑EB007825/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P41‑EB0019772/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01‑NS045062/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

