Identification of prognostic immunophenotypic features in cancer stromal cells of high-grade neuroendocrine carcinomas of the lung
- PMID: 24013219
- PMCID: PMC11824558
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-013-1502-5
Identification of prognostic immunophenotypic features in cancer stromal cells of high-grade neuroendocrine carcinomas of the lung
Abstract
Purpose: The immunophenotypes of cancer stromal cells have been recognized as prognostic factors of cancer. The purpose of this study was to analyze the prognostic markers of high-grade neuroendocrine carcinomas of the lung (HGNEC; both small cell carcinoma and large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma) by examining the immunophenotypes of cancer stromal cells.
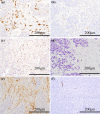
Materials and methods: One hundred and fifteen patients who underwent a complete resection of HGNEC were included in this study. We examined the presence of CD204-positive tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), Foxp3-positive regulatory T cells (Tregs), and podoplanin-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) to evaluate the prognostic values of these markers.
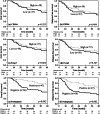
Results: The number of CD204-positive TAMs and Foxp3-positive Tregs did not influence the overall survival (OS) or the relapse-free survival (RFS) of the patients. However, patients with podoplanin-positive CAFs had a significantly better prognosis than those with podoplanin-negative CAFs [OS: p = 0.002, RFS: p = 0.002, 5-year overall survival (5YR): 74 vs. 45 %]. According to subgroup analyses, patients with podoplanin-positive CAFs displayed a better prognosis for both small cell carcinoma (OS: p = 0.046, 5YR: 74 vs. 46 %) and large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (OS: p = 0.020, 5YR: 74 vs. 45 %). Moreover, in multivariate analyses, the podoplanin status of the CAFs was shown to be a statistically significant independent predictor of recurrence.
Conclusion: The presence of podoplanin-positive CAFs had a favorable prognostic value, suggesting that the evaluation of podoplanin expression by CAFs would lead to a novel risk classification of patients.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The association of intravascular stromal cells with prognosis in high-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016 May;142(5):905-12. doi: 10.1007/s00432-015-2098-8. Epub 2015 Dec 22. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26696594 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological significance of cancer stem-like cell markers in high-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015 Dec;141(12):2121-30. doi: 10.1007/s00432-015-1985-3. Epub 2015 May 12. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25963795 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of podoplanin-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts in surgically resected primary lung adenocarcinoma predicts a shorter progression-free survival period in patients with recurrences who received platinum-based chemotherapy.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015 Jul;141(7):1163-70. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1891-0. Epub 2014 Dec 2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25446816 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The regulation of cancer-associated thrombosis by podoplanin.Thromb Update. 2024 Jun;15:100174. doi: 10.1016/j.tru.2024.100174. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Thromb Update. 2024. PMID: 40741180 Free PMC article.
-
The Significance of SPP1 in Lung Cancers and Its Impact as a Marker for Protumor Tumor-Associated Macrophages.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 12;15(8):2250. doi: 10.3390/cancers15082250. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37190178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Are Markers of Systemic Inflammatory Response Useful in the Management of Patients With Neuroendocrine Neoplasms?Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jul 22;12:672499. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.672499. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34367064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The association of intravascular stromal cells with prognosis in high-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016 May;142(5):905-12. doi: 10.1007/s00432-015-2098-8. Epub 2015 Dec 22. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26696594 Free PMC article.
-
Ankyrin Repeat Domain 1 Overexpression is Associated with Common Resistance to Afatinib and Osimertinib in EGFR-mutant Lung Cancer.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 5;8(1):14896. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33190-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30291293 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asamura H, Kameya T, Matsuno Y, Noguchi M, Tada H, Ishikawa Y, Yokose T, Jiang SX, Inoue T, Nakagawa K, Tajima K, Nagai K (2006) Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the lung: a prognostic spectrum. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 24(1):70–76. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.04.1202 - PubMed
-
- Bremnes RM, Donnem T, Al-Saad S, Al-Shibli K, Andersen S, Sirera R, Camps C, Marinez I, Busund LT (2011) The role of tumor stroma in cancer progression and prognosis: emphasis on carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol Off Publ Int Assoc Study Lung Cancer 6(1):209–217. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181f8a1bd - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

