DNA-PKcs inhibition sensitizes cancer cells to carbon-ion irradiation via telomere capping disruption
- PMID: 24013362
- PMCID: PMC3754927
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072641
DNA-PKcs inhibition sensitizes cancer cells to carbon-ion irradiation via telomere capping disruption
Abstract
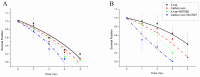
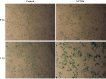
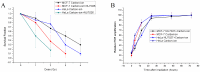
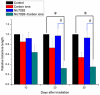
Heavy-ion irradiation induces a higher frequency of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) which must be properly repaired. Critical shortening of telomeres can trigger DNA damage responses such as DSBs. Telomeres are very sensitive to oxidative stress such as ionizing radiation. The DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) is the central component in the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) repair complex and participates in telomere maintenance. Therefore, it is expected to enhance the cell killing effect of heavy-ion irradiation via DNA-PKcs inhibition. To test this hypothesis, cellular radiosensitivity was measured by the clonal genetic assay. DNA damage repair was relatively quantified by long PCR. Apoptosis was quantified by flow-cytometric analysis of annexin V/PI double staining, and senescence was analyzed by galactosidase activity. Telomere length was semi-quantified by real-time PCR. P53 and p21 expression was determined by western blotting. Our data demonstrated that MCF-7 and HeLa cells with DNA-PKcs inhibition were more susceptible to carbon-ion irradiation than Those without DNA-PKcs inhibition. Even though NHEJ was inhibited by the DNA-PKcs specific inhibitor, NU7026, most DNA damage induced by carbon-ion irradiation was repaired within 24 hours after irradiation in both cell lines. However, potential lethal damage repair (PLDR) could not restore cellular inactivation in DNA-PKcs inhibited cells. MCF-7 cells showed extensive senescence and accelerated telomere length reduction, while HeLa cells underwent significant apoptosis after irradiation with NU7026 incubation. In addition, both cell lines with shorter telomere were more susceptible to carbon-ion radiation. Our current data suggested that DNA-PKcs inhibition could enhance cellular sensitivity to carbon-ion radiation via disturbing its functional role in telomere end protection. The combination of DNA-PKcs inhibition and carbon-ion irradiation may be an efficient method of heavy-ion therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
DNA-dependent protein kinase in telomere maintenance and protection.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2020 Jan 17;25:2. doi: 10.1186/s11658-020-0199-0. eCollection 2020. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2020. PMID: 31988640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic Roles of Non-Homologous End Joining and Homologous Recombination in Repair of Ionizing Radiation-Induced DNA Double Strand Breaks in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells.Cells. 2024 Aug 30;13(17):1462. doi: 10.3390/cells13171462. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39273031 Free PMC article.
-
Genistein sensitizes glioblastoma cells to carbon ions via inhibiting DNA-PKcs phosphorylation and subsequently repressing NHEJ and delaying HR repair pathways.Radiother Oncol. 2018 Oct;129(1):84-94. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2018.04.005. Epub 2018 Apr 21. Radiother Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29685705
-
DNA-PKcs Inhibition Sensitizes Human Chondrosarcoma Cells to Carbon Ion Irradiation via Cell Cycle Arrest and Telomere Capping Disruption.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 4;25(11):6179. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116179. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892366 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-PKcs: A promising therapeutic target in human hepatocellular carcinoma?DNA Repair (Amst). 2016 Nov;47:12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2016.10.004. Epub 2016 Oct 15. DNA Repair (Amst). 2016. PMID: 27789167 Review.
Cited by
-
Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoproteins Involved in the Functioning of Telomeres in Malignant Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 10;20(3):745. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030745. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30744200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiobiological effects of the alpha emitter Ra-223 on tumor cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 6;9(1):18489. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54884-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31811257 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-dependent protein kinase in telomere maintenance and protection.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2020 Jan 17;25:2. doi: 10.1186/s11658-020-0199-0. eCollection 2020. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2020. PMID: 31988640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combining carbon ion irradiation and non-homologous end-joining repair inhibitor NU7026 efficiently kills cancer cells.Radiat Oncol. 2015 Nov 9;10:225. doi: 10.1186/s13014-015-0536-z. Radiat Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26553138 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing Photon and Charged Particle Therapy Using DNA Damage Biomarkers.Int J Part Ther. 2018 Summer;5(1):15-24. doi: 10.14338/IJPT-18-00018.1. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Int J Part Ther. 2018. PMID: 31773017 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Deng W, Tsao SW, Guan XY, Lucas JN, Si HX, et al. (2004) Distinct profiles of critically short telomeres are a key determinant of different chromosome aberrations in immortalized human cells: whole-genome evidence from multiple cell lines. Oncogene 23: 9090–9101. - PubMed
-
- Zaal A, Louwers J, Berkhof J, Kocken M, Ter Harmsel W, et al... (2012) Agreement between colposcopic impression and histological diagnosis among human papillomavirus type 16-positive women: a clinical trial using dynamic spectral imaging colposcopy. BJOG. - PubMed
-
- Hou YY, Toh MT, Wang X (2012) NBS1 deficiency promotes genome instability by affecting DNA damage signaling pathway and impairing telomere integrity. Cell Biochem Funct 30: 233–242. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Zhou J, Lim CU (2006) The role of NBS1 in DNA double strand break repair, telomere stability, and cell cycle checkpoint control. Cell Res 16: 45–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

