Bicistronic gene transfer tools for delivery of miRNAs and protein coding sequences
- PMID: 24013374
- PMCID: PMC3794778
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms140918239
Bicistronic gene transfer tools for delivery of miRNAs and protein coding sequences
Abstract
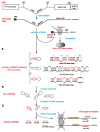
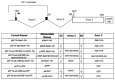
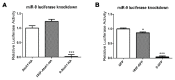
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a category of small RNAs that modulate levels of proteins via post-transcriptional inhibition. Currently, a standard strategy to overexpress miRNAs is as mature miRNA duplexes, although this method is cumbersome if multiple miRNAs need to be delivered. Many of these miRNAs are found within introns and processed through the RNA polymerase II pathway. We have designed a vector to exploit this naturally-occurring intronic pathway to deliver the three members of the sensory-specific miR-183 family from an artificial intron. In one version of the vector, the downstream exon encodes the reporter (GFP) while another version encodes a fusion protein created between the transcription factor Atoh1 and the hemaglutinin epitope, to distinguish it from endogenous Atoh1. In vitro analysis shows that the miRNAs contained within the artificial intron are processed and bind to their targets with specificity. The genes downstream are successfully translated into protein and identifiable through immunofluorescence. More importantly, Atoh1 is proven functional through in vitro assays. These results suggest that this cassette allows expression of miRNAs and proteins simultaneously, which provides the opportunity for joint delivery of specific translational repressors (miRNA) and possibly transcriptional activators (transcription factors). This ability is attractive for future gene therapy use.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A multiplexed miRNA and transgene expression platform for simultaneous repression and expression of protein coding sequences.Mol Biosyst. 2016 Jan;12(1):295-312. doi: 10.1039/c5mb00506j. Mol Biosyst. 2016. PMID: 26617199
-
Assessing the functional association of intronic miRNAs with their host genes.RNA. 2018 Aug;24(8):991-1004. doi: 10.1261/rna.064386.117. Epub 2018 May 11. RNA. 2018. PMID: 29752351 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Silencing In Vitro and In Vivo Using Intronic MicroRNAs.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1733:107-126. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7601-0_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29435927
-
Intron-mediated RNA interference and microRNA biogenesis.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;487:387-413. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-547-7_19. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19301658 Review.
-
Gene silencing in vitro and in vivo using intronic microRNAs.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;342:295-312. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-123-1:295. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16957384 Review.
Cited by
-
Viral Ubiquitin Ligase Stimulates Selective Host MicroRNA Expression by Targeting ZEB Transcriptional Repressors.Viruses. 2017 Aug 7;9(8):210. doi: 10.3390/v9080210. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 28783105 Free PMC article.
-
Trans-amplifying RNA expressing functional miRNA mediates target gene suppression and simultaneous transgene expression.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Mar 5;35(2):102162. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102162. eCollection 2024 Jun 11. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 38545619 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial on the Special Issue: Regulation by non-coding RNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Nov 6;14(11):21960-4. doi: 10.3390/ijms141121960. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24201126 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and Misexpression of the miR-183 Family in the Developing Hearing Organ of the Chicken.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 15;10(7):e0132796. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132796. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26176784 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNA as regulators of cardiac fibrosis: current insight and the road ahead.Pflugers Arch. 2016 Jun;468(6):1103-11. doi: 10.1007/s00424-016-1792-y. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Pflugers Arch. 2016. PMID: 26786602 Review.
References
-
- Ying S.Y., Lin S.L. Intron-mediated RNA interference and microRNA biogenesis. In: Sioud M., editor. Methods of Molecular Biology, siRNA and miRNA Gene Silencing. Vol. 487. Humana Press; New York, NY, USA: 2009. pp. 387–413. - PubMed
-
- Furukawa N., Sakurai F., Katayama K., Seki N., Kawabata K., Mizuguchi H. Optimization of a microRNA expression vector for function analysis of microRNA. J. Control Release. 2011;150:94–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

