Online evaluation of novel choices by simultaneous representation of multiple memories
- PMID: 24013592
- PMCID: PMC4001211
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3515
Online evaluation of novel choices by simultaneous representation of multiple memories
Abstract
Prior experience is critical for decision-making. It enables explicit representation of potential outcomes and provides training to valuation mechanisms. However, we can also make choices in the absence of prior experience by merely imagining the consequences of a new experience. Using functional magnetic resonance imaging repetition suppression in humans, we examined how neuronal representations of novel rewards can be constructed and evaluated. A likely novel experience was constructed by invoking multiple independent memories in hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex. This construction persisted for only a short time period, during which new associations were observed between the memories for component items. Together, these findings suggest that, in the absence of direct experience, coactivation of multiple relevant memories can provide a training signal to the valuation system that allows the consequences of new experiences to be imagined and acted on.
Figures



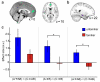
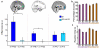

Comment in
-
Should I buy this book? How we construct prospective value.Nat Neurosci. 2013 Oct;16(10):1357-9. doi: 10.1038/nn.3521. Nat Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24067284 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wimmer GE, Shohamy D. Preference by association: how memory mechanisms in the hippocampus bias decisions. Science. 2012;338:270–273. - PubMed
-
- Peters J, Büchel C. Episodic future thinking reduces reward delay discounting through an enhancement of prefrontal-mediotemporal interactions. Neuron. 2010;66:138–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

