Characterisation of Lyzls in mice and antibacterial properties of human LYZL6
- PMID: 24013621
- PMCID: PMC3854060
- DOI: 10.1038/aja.2013.93
Characterisation of Lyzls in mice and antibacterial properties of human LYZL6
Abstract
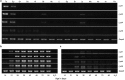
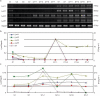
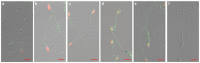
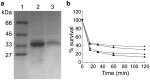
C-type lysozyme genes (Lyzls) belong to the class of lysozymes and are highly expressed in the testis and epididymis. The members Lyzl4 and Spaca3 have been reported to play a role in sperm-egg binding and fertilisation in mice. However, the function of the remaining two mouse c-type lysozyme genes, Lyzl1 and Lyzl6, is still not clear. In the present study, we analysed the tissue expression and androgen-dependent expression of mouse c-type lysozyme genes and the possible contribution of human recombinant LYZL6 (rLYZL6) to immunity. The expression of Lyzls was detected by RT-PCR, Western blots, immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence. The bacteriolytic activity of rLYZL6 was analysed by a colony-forming assay. In mice, the expression of Lyzl genes was mainly in the testis and epididymis in a developmentally regulated manner and androgen- or testicular factor-regulated manner. Immunodetection revealed the presence of LYZL6 protein in primary spermatocytes and round spermatids of the testis and on the post-acrosomal area and midpiece of mature epididymal spermatozoa. The rLYZL6 protein exhibited antibacterial activity. From the results, Lyzls may play a role in mitochondrial function of spermatozoa and LYZL6 may contribute to the innate immunity of the male genital tract.
Figures

References
-
- Fleming A. On a remarkable bacteriolytic element found in tissues and secretions. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1922;93:306–17.
-
- Jollès P, Jollès J. What's new in lysozyme research? Always a model system, today as yesterday. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984;63:165–89. - PubMed
-
- Prager EM, Jollès P. Animal lysozymes c and g: an overview. EXS. 1996;75:9–31. - PubMed
-
- Zhang K, Gao R, Zhang H, Cai X, Shen C, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of three novel lysozyme-like genes, predominantly expressed in the male reproductive system of humans, belonging to the c-type lysozyme/alpha-lactalbumin family. Biol Reprod. 2005;73:1064–71. - PubMed
-
- Prager EM. Adaptive evolution of lysozyme: changes in amino acid sequence, regulation of expression and gene number. EXS. 1996;75:323–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

