Commentary: Pediatric obesity: systems science strategies for prevention
- PMID: 24013965
- PMCID: PMC3888301
- DOI: 10.1093/jpepsy/jst071
Commentary: Pediatric obesity: systems science strategies for prevention
Abstract
Objectives: Pediatric obesity is a major public health problem that undermines the physical and mental health of children and increases their risk for adult obesity and other chronic illnesses. Although health care providers, including pediatric psychologists, have implemented prevention programs, effects have been minimal, with no solid evidence of sustainable programs.
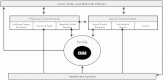
Methods: A systems science framework that incorporates the multiple interacting factors that influence pediatric obesity may be useful in guiding prevention.
Results: The National Prevention Strategy provides recommendations that can be incorporated into systems science designs, including (1) Healthy and Safe Environments, (2) Clinical and Community Preventive Services, (3) Empowering People, and (4) Elimination of Health Disparities. In addition, our recommendation is that future obesity prevention programs target early in life (pre-pregnancy through toddlerhood) and use multilevel multidisciplinary designs.
Conclusions: The benefits of preventing pediatric obesity extend from the health and well-being of individual children to the economic security of the nation.
Figures
References
-
- Anzman-Frasca S, Stifter C A, Birch L L. Temperament and childhood obesity risk: A review of the literature. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics. 2012;33:732–745. - PubMed
-
- Barlow S E. Expert committee recommendations regarding the prevention, assessment, and treatment of child and adolescent overweight and obesity: Summary report. Pediatrics. 2007;120(Suppl 4):S164–S192. - PubMed
-
- Berkowitz R I, Rukstalis M R, Bishop-Gilyard C T, Moore R H, Gehrman C A, Xanthopoulos M S, Cochran W J, Louden D, Wadden T A. Treatment of adolescent obesity comparing self-guided and group lifestyle modification programs: A potential model for primary care. Journal of Pediatric Psychology. 2013;38:978–986. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bronfenbrenner U, Ceci S J. Nature-nurture reconceptualized in developmental perspective: A bioecological model. Psychological Review. 1994;101:568–586. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical