Transgenic expression of microRNA-185 causes a developmental arrest of T cells by targeting multiple genes including Mzb1
- PMID: 24014023
- PMCID: PMC3798545
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.503532
Transgenic expression of microRNA-185 causes a developmental arrest of T cells by targeting multiple genes including Mzb1
Abstract
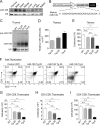
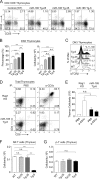
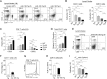
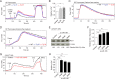
miR-185 is a microRNA (miR) that targets Bruton's tyrosine kinase in B cells, with reductions in miR-185 linked to B cell autoantibody production. In hippocampal neurons, miR-185 targets both sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2 and a novel Golgi inhibitor. This miR is haploinsufficient in 90-95% of individuals with chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome, patients who can present with immune, cardiac, and parathyroid problems, learning disorders, and a high incidence of schizophrenia in adults. The reduced levels of miR-185 in neurons cause presynaptic neurotransmitter release. Many of the 22q11.2 deletion syndrome patients have a thymic hypoplasia, which results in a peripheral T cell lymphopenia and unusual T helper cell skewing. The molecular targets of miR-185 in thymocytes are unknown. Using an miR-185 T cell transgenic approach, increasing levels of miR-185 attenuated T cell development at the T cell receptor β (TCRβ) selection checkpoint and during positive selection. This caused a peripheral T cell lymphopenia. Mzb1, Nfatc3, and Camk4 were identified as novel miR-185 targets. Elevations in miR-185 enhanced TCR-dependent intracellular calcium levels, whereas a knockdown of miR-185 diminished these calcium responses. These effects concur with reductions in Mzb1, an endoplasmic reticulum calcium regulator. Consistent with their haploinsufficiency of miR-185, Mzb1 levels were elevated in thymocyte extracts from several 22q11.2 deletion syndrome patients. Our findings indicate that miR-185 regulates T cell development through its targeting of several mRNAs including Mzb1.
Keywords: 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome; Calcium Intracellular Release; Genetic Diseases; Immunodeficiency; MicroRNA; T Cell Biology; Transcription Target Genes; Transgenic Mice.
Figures


References
-
- Bartel D. P. (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116, 281–297 - PubMed
-
- Kloosterman W. P., Plasterk R. H. (2006) The diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease. Dev. Cell 11, 441–450 - PubMed
-
- Papadopoulou A. S., Dooley J., Linterman M. A., Pierson W., Ucar O., Kyewski B., Zuklys S., Hollander G. A., Matthys P., Gray D. H., De Strooper B., Liston A. (2012) The thymic epithelial microRNA network elevates the threshold for infection-associated thymic involution via miR-29a mediated suppression of the IFN-α receptor. Nat. Immunol. 13, 181–187 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

