Dynamic analysis of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor-ErbB2-ErbB3 protein network by luciferase fragment complementation imaging
- PMID: 24014028
- PMCID: PMC3798547
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.489534
Dynamic analysis of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor-ErbB2-ErbB3 protein network by luciferase fragment complementation imaging
Abstract
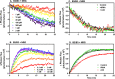
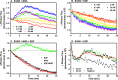
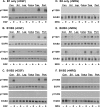
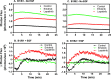
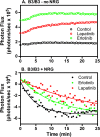
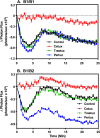
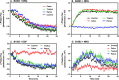
ErbB3 is a member of the ErbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases. It is unique because it is the only member of the family whose kinase domain is defective. As a result, it is obliged to form heterodimers with other ErbB receptors to signal. In this study, we characterized the interaction of ErbB3 with the EGF receptor and ErbB2 and assessed the effects of Food and Drug Administration-approved therapeutic agents on these interactions. Our findings support the concept that ErbB3 exists in preformed clusters that can be dissociated by NRG-1β and that it interacts with other ErbB receptors in a distinctly hierarchical fashion. Our study also shows that all pairings of the EGF receptor, ErbB2, and ErbB3 form ligand-independent dimers/oligomers. The small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors erlotinib and lapatinib differentially enhance the dimerization of the various ErbB receptor pairings, with the EGFR/ErbB3 heterodimer being particularly sensitive to the effects of erlotinib. The data suggest that the physiological effects of these drugs may involve not only inhibition of tyrosine kinase activity but also a dynamic restructuring of the entire network of receptors.
Keywords: Cancer Biology; Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF); Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR); ErbB2; ErbB3; Growth Factors; Receptor Tyrosine Kinase.
Figures



References
-
- Garrett T. P., McKern N. M., Lou M., Elleman T. C., Adams T. E., Lovrecz G. O., Zhu H.-J., Walker F., Frenkel M. J., Hoyne P. A., Jorissen R. N., Nice E. C., Burgess A. W., Ward C. W. (2002) Crystal Structure of a truncated epidermal growth factor receptor extracellular domain bound to transforming growth factor a. Cell 110, 763–773 - PubMed
-
- Ogiso H., Ishitani R., Nureki O., Fukai S., Yamanaka M., Kim J.-H., Saito K., Sakamoto A., Inoue M., Shirouzu M., Yokoyama S. (2002) Crystal structure of the complex of human epidermal growth factor and receptor extracellular domains. Cell 110, 775–787 - PubMed
-
- Ferguson K. M., Berger M. B., Mendrola J. M., Cho H.-S., Leahy D. J., Lemmon M. A. (2003) EGF Activates its receptor by removing interactions that autoinhibit ectodomain dimerization. Mol. Cell 11, 507–517 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

