Dual positive feedback regulation of protein degradation of an extra-cytoplasmic function σ factor for cell differentiation in Streptomyces coelicolor
- PMID: 24014034
- PMCID: PMC3829432
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.491498
Dual positive feedback regulation of protein degradation of an extra-cytoplasmic function σ factor for cell differentiation in Streptomyces coelicolor
Abstract
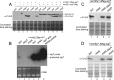
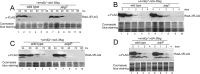
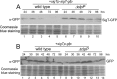
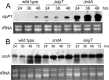
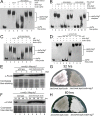
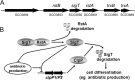
Here we report that in Streptomyces coelicolor, the protein stability of an ECF σ factor SigT, which is involved in the negative regulation of cell differentiation, was completely dependent on its cognate anti-σ factor RstA. The degradation of RstA caused a ClpP/SsrA-dependent degradation of SigT during cell differentiation. This was consistent with the delayed morphological development or secondary metabolism in the ΔclpP background after rstA deletion or sigT overexpression. Meanwhile, SigT negatively regulated clpP/ssrA expression by directly binding to the clpP promoter (clpPp). The SigT-clpPp interaction could be disrupted by secondary metabolites, giving rise to the stabilized SigT protein and retarded morphological development in a non-antibiotic-producing mutant. Thus a novel regulatory mechanism was revealed that the protein degradation of the ECF σ factor was initiated by the degradation of its anti-σ factor, and was accelerated in a dual positive feedback manner, through regulation by secondary metabolites, to promote rapid and irreversible development of the secondary metabolism. This ingenious cooperation of intracellular components can ensure economical and exquisite control of the ECF σ factor protein level for the proper cell differentiation in Streptomyces.
Keywords: Actinobacteria; Antibiotics; Protein Degradation; Secondary Metabolism; Transcription Regulation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Proteasome involvement in a complex cascade mediating SigT degradation during differentiation of Streptomyces coelicolor.FEBS Lett. 2014 Feb 14;588(4):608-13. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.12.029. Epub 2014 Jan 17. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24440356
-
Involvement of SigT and RstA in the differentiation of Streptomyces coelicolor.FEBS Lett. 2009 Oct 6;583(19):3145-50. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.09.025. Epub 2009 Sep 13. FEBS Lett. 2009. PMID: 19755120
-
The ECF sigma factor SigT regulates actinorhodin production in response to nitrogen stress in Streptomyces coelicolor.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011 Dec;92(5):1009-21. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3619-2. Epub 2011 Oct 16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 22002068
-
SigR, a hub of multilayered regulation of redox and antibiotic stress responses.Mol Microbiol. 2019 Aug;112(2):420-431. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14341. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Mol Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31269533 Review.
-
The extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factors.Adv Microb Physiol. 2002;46:47-110. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(02)46002-x. Adv Microb Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12073657 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracytoplasmic Function σ Factors Can Be Implemented as Robust Heterologous Genetic Switches in Bacillus subtilis.iScience. 2019 Mar 29;13:380-390. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.03.001. Epub 2019 Mar 5. iScience. 2019. PMID: 30897511 Free PMC article.
-
RskA Is a Dual Function Activator-Inhibitor That Controls SigK Activity Across Distinct Bacterial Genera.Front Microbiol. 2020 Sep 9;11:558166. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.558166. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33013790 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of a stable sigma factor SigR by translation-inhibiting antibiotics confers resistance to antibiotics.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 27;6:28628. doi: 10.1038/srep28628. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27346454 Free PMC article.
-
Degradation Mechanism of AAA+ Proteases and Regulation of Streptomyces Metabolism.Biomolecules. 2022 Dec 10;12(12):1848. doi: 10.3390/biom12121848. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36551276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of Series of Affinity Tags in Streptomyces.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 31;7(1):6854. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07377-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28761057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gruber T. M., Gross C. A. (2003) Multiple σ subunits and the partitioning of bacterial transcription space. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 57, 441–466 - PubMed
-
- Staroń A., Sofia H. J., Dietrich S., Ulrich L. E., Liesegang H., Mascher T. (2009) The third pillar of bacterial signal transduction. Classification of the extracytoplasmic function (ECF) σ factor protein family. Mol. Microbiol. 74, 557–581 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

