Dual positive feedback regulation of protein degradation of an extra-cytoplasmic function σ factor for cell differentiation in Streptomyces coelicolor
- PMID: 24014034
- PMCID: PMC3829432
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.491498
Dual positive feedback regulation of protein degradation of an extra-cytoplasmic function σ factor for cell differentiation in Streptomyces coelicolor
Abstract
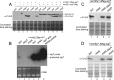
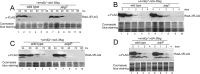
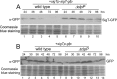
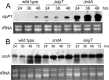
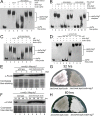
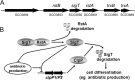
Here we report that in Streptomyces coelicolor, the protein stability of an ECF σ factor SigT, which is involved in the negative regulation of cell differentiation, was completely dependent on its cognate anti-σ factor RstA. The degradation of RstA caused a ClpP/SsrA-dependent degradation of SigT during cell differentiation. This was consistent with the delayed morphological development or secondary metabolism in the ΔclpP background after rstA deletion or sigT overexpression. Meanwhile, SigT negatively regulated clpP/ssrA expression by directly binding to the clpP promoter (clpPp). The SigT-clpPp interaction could be disrupted by secondary metabolites, giving rise to the stabilized SigT protein and retarded morphological development in a non-antibiotic-producing mutant. Thus a novel regulatory mechanism was revealed that the protein degradation of the ECF σ factor was initiated by the degradation of its anti-σ factor, and was accelerated in a dual positive feedback manner, through regulation by secondary metabolites, to promote rapid and irreversible development of the secondary metabolism. This ingenious cooperation of intracellular components can ensure economical and exquisite control of the ECF σ factor protein level for the proper cell differentiation in Streptomyces.
Keywords: Actinobacteria; Antibiotics; Protein Degradation; Secondary Metabolism; Transcription Regulation.
Figures


References
-
- Gruber T. M., Gross C. A. (2003) Multiple σ subunits and the partitioning of bacterial transcription space. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 57, 441–466 - PubMed
-
- Staroń A., Sofia H. J., Dietrich S., Ulrich L. E., Liesegang H., Mascher T. (2009) The third pillar of bacterial signal transduction. Classification of the extracytoplasmic function (ECF) σ factor protein family. Mol. Microbiol. 74, 557–581 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

