Effects of eugenol on T-type Ca2+ channel isoforms
- PMID: 24014106
- PMCID: PMC11047949
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.113.207936
Effects of eugenol on T-type Ca2+ channel isoforms
Abstract
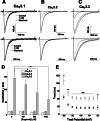
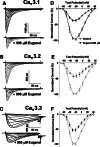
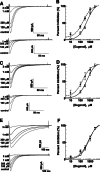
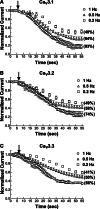
Eugenol has been used as an analgesic in dentistry. Previous studies have demonstrated that voltage-gated Na(+) channels and high-voltage-activated Ca(2+) channels expressed in trigeminal ganglion (TG) neurons sensing dental pain are molecular targets of eugenol for its analgesic effects. However, it has not been investigated whether eugenol can affect T-type Ca(2+) channels, which are known to be detected in the afferent neurons. In this report, we investigate how eugenol can influence cloned T-type channel isoforms expressed in HEK293 cells, using whole-cell patch clamp. Application of eugenol inhibited Cav3.1, Cav3.2, and Cav3.3 currents in a concentration-dependent manner with IC50 values of 463, 486, and 708 μM, respectively. Eugenol was found to negatively shift the steady-state inactivation curves of the T-type channel isoforms, but it did not shift their activation curves. In addition, eugenol had little effect on the current kinetics of Cav3.1 and Cav3.2, but it accelerated the inactivation kinetics of Cav3.3 currents. Reduction of channel availability enhanced eugenol inhibition sensitivity for Cav3.1 and Cav3.2, but not for Cav3.3. Moreover, eugenol inhibition of T-type channel isoforms was found to be use dependent. Finally, we show that the T-type currents recorded from rat TG neurons were inhibited by eugenol with a similar potency to Cav3.1 and Cav3.2 isoforms. Taken together, our findings suggest that T-type Ca(2+) channels are additional molecular targets for the pain-relieving effects of eugenol.
Figures


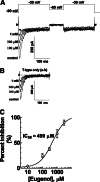

Similar articles
-
T-type calcium channel inhibition underlies the analgesic effects of the endogenous lipoamino acids.J Neurosci. 2009 Oct 21;29(42):13106-14. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2919-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19846698 Free PMC article.
-
Eugenol inhibits calcium currents in dental afferent neurons.J Dent Res. 2005 Sep;84(9):848-51. doi: 10.1177/154405910508400913. J Dent Res. 2005. PMID: 16109996
-
Melatonin-mediated inhibition of Cav3.2 T-type Ca2+ channels induces sensory neuronal hypoexcitability through the novel protein kinase C-eta isoform.J Pineal Res. 2018 May;64(4):e12476. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12476. Epub 2018 Mar 8. J Pineal Res. 2018. PMID: 29437250
-
T-type calcium channels: functional regulation and implication in pain signaling.J Pharmacol Sci. 2013;122(4):244-50. doi: 10.1254/jphs.13r05cp. Epub 2013 Aug 1. J Pharmacol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23903007 Review.
-
Regulation of the T-type Ca(2+) channel Cav3.2 by hydrogen sulfide: emerging controversies concerning the role of H2 S in nociception.J Physiol. 2016 Aug 1;594(15):4119-29. doi: 10.1113/JP270963. Epub 2016 Feb 25. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26804000 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plant and fungi derived analgesic natural products targeting voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels.Channels (Austin). 2022 Dec;16(1):198-215. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2022.2103234. Channels (Austin). 2022. PMID: 36017978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant-derived natural products targeting ion channels for pain.Neurobiol Pain. 2023 Apr 17;13:100128. doi: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2023.100128. eCollection 2023 Jan-Jul. Neurobiol Pain. 2023. PMID: 37151956 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-Application of Eugenol and QX-314 Elicits the Prolonged Blockade of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels in Nociceptive Trigeminal Ganglion Neurons.Biomolecules. 2020 Nov 5;10(11):1513. doi: 10.3390/biom10111513. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33167484 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Negative Allosteric Modulators of 5-HT₃ Receptors.Molecules. 2018 Dec 3;23(12):3186. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123186. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30513973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ins and outs of T-channel structure function.Pflugers Arch. 2014 Apr;466(4):627-33. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1419-5. Epub 2013 Dec 14. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 24337909 Review.
References
-
- Chen CC, Lamping KG, Nuno DW, Barresi R, Prouty SJ, Lavoie JL, Cribbs LL, England SK, Sigmund CD, Weiss RM, et al. (2003) Abnormal coronary function in mice deficient in alpha1H T-type Ca2+ channels. Science 302:1416–1418. - PubMed
-
- Ertel EA, Cohen CJ. (1994) Voltage-dependent interactions: the influence and significance of membrane potential on drug-receptor interactions. Drug Dev Res 33:204–213.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

