Evidence of serologic activity in chronic hepatitis B after surface antigen (HBsAg) seroclearance documented by conventional HBsAg assay
- PMID: 24014110
- PMCID: PMC3758508
- DOI: 10.1007/s12072-012-9354-7
Evidence of serologic activity in chronic hepatitis B after surface antigen (HBsAg) seroclearance documented by conventional HBsAg assay
Abstract
Background: Possible serologic activity after hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) seroclearance documented by conventional assays in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) has not been thoroughly investigated.
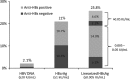
Methods: We determined the levels of serum hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA, hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg), and linearized HBsAg (CLEIA prototype) in 329 CHB patients (72.0% male) after HBsAg seroclearance was documented by a conventional HBsAg assay.
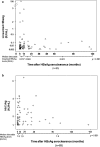
Results: The median interval between presentation and HBsAg seroclearance was 69.4 months. The median age at HBsAg seroclearance was 50 years. Assays for serum HBV DNA, HBcrAg, and linearized HBsAg were performed at a median time interval of 11.2 months after HBsAg loss. Linearized HBsAg and HBcrAg were detectable in 85 (25.8%) and 69 (21%) patients, respectively, and one or both serologic markers were detectable in 133 patients (40.4%). Serum HBV DNA was detectable in only 7 patients (2.1%). There was no correlation between linearized HBsAg and HBcrAg levels (r = 0.095, p = 0.924). The incidences of detectable linearized HBsAg and HBcrAg did not differ between patient samples taken at 6-12 and >12 months after HBsAg seroclearance (p = 0.146 and 0.079, respectively). Among patients with detectable serologic markers, median levels of linearized HBsAg (p = 0.581) and HBcrAg (p = 0.951) did not significantly change with time after HBsAg seroclearance.
Conclusion: Using novel HBcrAg and linearized HBsAg assays, viral serologic activity after HBsAg seroclearance was demonstrated in more than 40% of CHB patients. These tests have potential applications in diagnosing and prognosticating CHB patients with HBsAg seroclearance.
Keywords: HBcrAg; HBsAg; Linearized HBsAg; Seroclearance; Serology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Linearized hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B core-related antigen in the natural history of chronic hepatitis B.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014 Nov;20(11):1173-80. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12739. Epub 2014 Jul 29. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014. PMID: 24975365
-
A longitudinal study to detect hepatitis B surface and core-related antigens in chronic hepatitis B patients with hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance using highly sensitive assays.J Clin Virol. 2023 Mar;160:105375. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2022.105375. Epub 2022 Dec 23. J Clin Virol. 2023. PMID: 36623378
-
Potential of ultra-highly sensitive immunoassays for hepatitis B surface and core-related antigens in patients with or without development of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance.Hepatol Res. 2021 Apr;51(4):426-435. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13602. Epub 2021 Mar 6. Hepatol Res. 2021. PMID: 33270344
-
Progression and status of antiviral monitoring in patients with chronic hepatitis B: From HBsAg to HBV RNA.World J Hepatol. 2018 Sep 27;10(9):603-611. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v10.i9.603. World J Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 30310538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review article: hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg): an emerging marker for chronic hepatitis B virus infection.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Jan;47(1):43-54. doi: 10.1111/apt.14376. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29035003 Review.
Cited by
-
An overview of occult hepatitis B infection (OBI) with emphasis on HBV vaccination.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 28;10(17):e37097. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37097. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39281486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B core-related antigen: A novel and promising surrogate biomarker to guide anti-hepatitis B virus therapy.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023 Oct;29(4):851-868. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0434. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36891607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Biomarkers of Chronic Hepatitis B.Gut Liver. 2019 Nov 15;13(6):589-595. doi: 10.5009/gnl18425. Gut Liver. 2019. PMID: 30919601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel biomarkers for the management of chronic hepatitis B.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2020 Jul;26(3):261-279. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2020.0032. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32536045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Managing HBV and HCV Infection Pre- and Post-liver Transplant.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2024 Mar-Apr;14(2):101287. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2023.09.008. Epub 2023 Sep 23. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38076445 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

