Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) expression is increased in the subsynovial connective tissues of patients with idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome
- PMID: 24014274
- PMCID: PMC4095953
- DOI: 10.1002/jor.22485
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) expression is increased in the subsynovial connective tissues of patients with idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome
Abstract
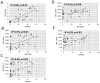
Non-inflammatory fibrosis of the subsynovial connective tissue (SSCT) is a hallmark of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). The etiology of this finding and its relationship to the development of CTS remain poorly understood. Recent studies have found that transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) plays a central role in fibrosis. The purpose of this study was to investigate the expression of TGF-β and connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), a downstream mediator of TGF-β, in the pathogenesis of CTS. We compared SSCT specimens from 26 idiopathic CTS patients with specimens from 10 human cadaver controls with no previous diagnosis of CTS. Immunohistochemistry was performed to determine levels TGF-β1, CTGF, collagen 1(Col1) and collagen 3 (Col3) expression. TGF-β1 (p < 0.01), CTGF (p < 0.01), and Col3 (p < 0.01) were increased in SSCT of CTS patients compared with control tissue. In addition, a strong positive correlation was found between TGF-β1 and CTGF, (R(2) = 0.80, p < 0.01) and a moderate positive correlation between Col3 and TGF-β1 (R(2) = 0.49, p < 0.01). These finding suggest that there is an increased expression of TGF-β and CTGF, a TGF-β regulated protein, and that this TGF-β activation may be responsible for SSCT fibrosis in CTS patients.
Keywords: CTGF; TGF-β; carpal tunnel syndrome; subsynovial connective tissue.
© 2013 Orthopaedic Research Society. Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


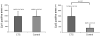
Similar articles
-
TGF-β signaling regulates fibrotic expression and activity in carpal tunnel syndrome.J Orthop Res. 2014 Nov;32(11):1444-50. doi: 10.1002/jor.22694. Epub 2014 Jul 30. J Orthop Res. 2014. PMID: 25073432 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) expression is increased in the subsynovial connective tissue in a rabbit model of carpal tunnel syndrome.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 30;9(9):e108312. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108312. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25269071 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking fibrotic signaling in fibroblasts from patients with carpal tunnel syndrome.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Mar;233(3):2067-2074. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25901. Epub 2017 May 3. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28294324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subsynovial connective tissue is sensitive to surgical interventions in a rabbit model of carpal tunnel syndrome.J Orthop Res. 2012 Apr;30(4):649-54. doi: 10.1002/jor.21565. Epub 2011 Oct 18. J Orthop Res. 2012. PMID: 22009518 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical evidence and mechanisms of growth factors in idiopathic and diabetes-induced carpal tunnel syndrome.Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Oct 15;837:156-163. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.08.017. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30125568 Review.
Cited by
-
Manual therapy prevents onset of nociceptor activity, sensorimotor dysfunction, and neural fibrosis induced by a volitional repetitive task.Pain. 2019 Mar;160(3):632-644. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001443. Pain. 2019. PMID: 30461558 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of a monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 synthesis inhibitor on fibroblasts from patients with carpal tunnel syndrome.J Orthop Sci. 2021 Mar;26(2):295-299. doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2020.03.010. Epub 2020 Apr 19. J Orthop Sci. 2021. PMID: 32317146 Free PMC article.
-
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome as an Early Underrecognized Feature of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Population-Based Study of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Occurrence Before and After Rheumatoid Arthritis Incidence.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2025 May 5:10.1002/acr.25566. doi: 10.1002/acr.25566. Online ahead of print. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2025. PMID: 40322852
-
Prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome in patients with long-term type 2 diabetes mellitus.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 22;8(12):e12615. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12615. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36593820 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the mechanism underlying hsa-miR338-3p downregulation to promote fibrosis of the synovial tissue in osteoarthritis patients.Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Feb;46(1):627-637. doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-4518-8. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30484106
References
-
- Donato G, Galasso O, Valentino P, et al. Pathological findings in subsynovial connective tissue in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin Neuropathol. 2009;28:129–135. - PubMed
-
- Schuind F, Ventura M, Pasteels JL. Idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome: histologic study of flexor tendon synovium. J Hand Surg Am. 1990;15:497–503. - PubMed
-
- Hirata H, Nagakura T, Tsujii M, et al. The relationship of VEGF and PGE2 expression to extracellular matrix remodelling of the tenosynovium in the carpal tunnel syndrome. J Pathol. 2004;204:605–612. - PubMed
-
- Ettema AM, Amadio PC, Zhao C, Wold LE, An KN. A histological and immunohistochemical study of the subsynovial connective tissue in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A:1458–1466. - PubMed
-
- Kim JK, Koh YD, Kim JS, Hann HJ, Kim MJ. Oxidative stress in subsynovial connective tissue of idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. J Orthop Res. 2010;28:1463–1468. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

