The value of magnetoencephalography for seizure-onset zone localization in magnetic resonance imaging-negative partial epilepsy
- PMID: 24014520
- PMCID: PMC3784280
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awt213
The value of magnetoencephalography for seizure-onset zone localization in magnetic resonance imaging-negative partial epilepsy
Abstract
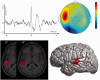
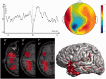
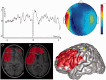
Surgical treatment of epilepsy is a challenge for patients with non-contributive brain magnetic resonance imaging. However, surgery is feasible if the seizure-onset zone is precisely delineated through intracranial electroencephalography recording. We recently described a method, volumetric imaging of epileptic spikes, to delineate the spiking volume of patients with focal epilepsy using magnetoencephalography. We postulated that the extent of the spiking volume delineated with volumetric imaging of epileptic spikes could predict the localizability of the seizure-onset zone by intracranial electroencephalography investigation and outcome of surgical treatment. Twenty-one patients with non-contributive magnetic resonance imaging findings were included. All patients underwent intracerebral electroencephalography investigation through stereotactically implanted depth electrodes (stereo-electroencephalography) and magnetoencephalography with delineation of the spiking volume using volumetric imaging of epileptic spikes. We evaluated the spatial congruence between the spiking volume determined by magnetoencephalography and the localization of the seizure-onset zone determined by stereo-electroencephalography. We also evaluated the outcome of stereo-electroencephalography and surgical treatment according to the extent of the spiking volume (focal, lateralized but non-focal or non-lateralized). For all patients, we found a spatial overlap between the seizure-onset zone and the spiking volume. For patients with a focal spiking volume, the seizure-onset zone defined by stereo-electroencephalography was clearly localized in all cases and most patients (6/7, 86%) had a good surgical outcome. Conversely, stereo-electroencephalography failed to delineate a seizure-onset zone in 57% of patients with a lateralized spiking volume, and in the two patients with bilateral spiking volume. Four of the 12 patients with non-focal spiking volumes were operated upon, none became seizure-free. As a whole, patients having focal magnetoencephalography results with volumetric imaging of epileptic spikes are good surgical candidates and the implantation strategy should incorporate volumetric imaging of epileptic spikes results. On the contrary, patients with non-focal magnetoencephalography results are less likely to have a localized seizure-onset zone and stereo electroencephalography is not advised unless clear localizing information is provided by other presurgical investigation methods.
Keywords: EEG; MEG; epilepsy surgery; epileptogenic zone; intracranial EEG; partial seizures.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship between morphological lesion, magnetic source imaging, and intracranial stereo-electroencephalography in focal cortical dysplasia.Neuroimage Clin. 2017 Apr 20;15:71-79. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2017.04.018. eCollection 2017. Neuroimage Clin. 2017. PMID: 28491494 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetoencephalography-directed surgery in patients with neocortical epilepsy.J Neurosurg. 2002 Oct;97(4):865-73. doi: 10.3171/jns.2002.97.4.0865. J Neurosurg. 2002. PMID: 12405375 Clinical Trial.
-
Accuracy of MEG in localizing irritative zone and seizure onset zone: Quantitative comparison between MEG and intracranial EEG.Epilepsy Res. 2016 Nov;127:291-301. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2016.08.013. Epub 2016 Aug 16. Epilepsy Res. 2016. PMID: 27693985
-
Role of magnetoencephalography and stereo-electroencephalography in the presurgical evaluation in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy.Neurol India. 2017;65(Supplement):S34-S44. doi: 10.4103/0028-3886.201680. Neurol India. 2017. PMID: 28281494 Review.
-
Surgical treatment of medically refractory epilepsy in childhood.Brain Dev. 2001 Jul;23(4):199-207. doi: 10.1016/s0387-7604(01)00204-2. Brain Dev. 2001. PMID: 11376996 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of MEG results on surgical outcomes in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy associated with focal encephalomalacia: a single-center experience.J Neurol. 2020 Mar;267(3):812-822. doi: 10.1007/s00415-019-09638-w. Epub 2019 Nov 26. J Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31773245
-
Accuracy and spatial properties of distributed magnetic source imaging techniques in the investigation of focal epilepsy patients.Hum Brain Mapp. 2020 Aug 1;41(11):3019-3033. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24994. Epub 2020 May 9. Hum Brain Mapp. 2020. PMID: 32386115 Free PMC article.
-
Reproducibility of EEG-MEG fusion source analysis of interictal spikes: Relevance in presurgical evaluation of epilepsy.Hum Brain Mapp. 2018 Feb;39(2):880-901. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23889. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Hum Brain Mapp. 2018. PMID: 29164737 Free PMC article.
-
Misdirection due to early magnetoencephalographic presentation and management in Rasmussen encephalitis: a case report.Front Neurol. 2023 Nov 30;14:1261104. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1261104. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 38099072 Free PMC article.
-
Intracranial EEG potentials estimated from MEG sources: A new approach to correlate MEG and iEEG data in epilepsy.Hum Brain Mapp. 2016 May;37(5):1661-83. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23127. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Hum Brain Mapp. 2016. PMID: 26931511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agirre-Arrizubieta Z, Huiskamp GJ, Ferrier CH, van Huffelen AC, Leijten FS. Interictal magnetoencephalography and the irritative zone in the electrocorticogram. Brain. 2009;132(Pt 11):3060–71. - PubMed
-
- Bancaud J, Angelergues R, Bernouilli C, Bonis A, Bordas-Ferrer M, Bresson M, et al. [Functional stereotaxic exploration (stereo-electroencephalography) in epilepsies] Rev Neurol (Paris) 1969;120:448. - PubMed
-
- Berg AT, Vickrey BG, Langfitt JT, Sperling MR, Walczak TS, Shinnar S, et al. The multicenter study of epilepsy surgery: recruitment and selection for surgery. Epilepsia. 2003;44:1425–33. - PubMed
-
- Bouet R, Jung J, Delpuech C, Ryvlin P, Isnard J, Guenot M, et al. Towards source volume estimation of interictal spikes in focal epilepsy using magnetoencephalography. Neuroimage. 2012;59:3955–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

