A new approach to species delimitation in Septoria
- PMID: 24014901
- PMCID: PMC3713889
- DOI: 10.3114/sim0018
A new approach to species delimitation in Septoria
Abstract
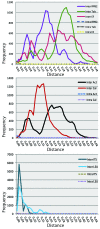
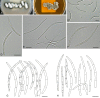
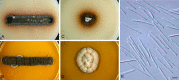
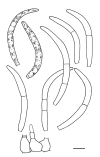
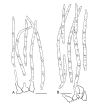
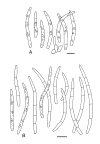
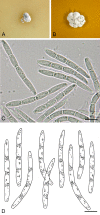
Septoria is a large genus of asexual morphs of Ascomycota causing leaf spot diseases of many cultivated and wild plants. Host specificity has long been a decisive criterium in species delimitation in Septoria, mainly because of the paucity of useful morphological characters and the high level of variation therein. This study aimed at improving the species delimitation of Septoria by adopting a polyphasic approach, including multilocus DNA sequencing and morphological analyses on the natural substrate and in culture. To this end 365 cultures preserved in CBS, Utrecht, The Netherlands, among which many new isolates obtained from fresh field specimens were sequenced. Herbarium material including many types was also studied. Full descriptions of the morphology in planta and in vitro are provided for 57 species. DNA sequences were generated for seven loci, viz. nuclear ITS and (partial) LSU ribosomal RNA genes, RPB2, actin, calmodulin, Btub, and EF. The robust phylogeny inferred showed that the septoria-like fungi are distributed over three main clades, establishing the genera Septoria s. str., Sphaerulina, and Caryophylloseptoria gen. nov. Nine new combinations and one species, Sphaerulina tirolensis sp. nov. were proposed. It is demonstrated that some species have wider host ranges than expected, including hosts from more than one family. Septoria protearum, previously only associated with Proteaceae was found to be also associated with host plants from six additional families of phanerogams and cryptogams. To our knowledge this is the first study to provide DNA-based evidence that multiple family-associations occur for a single species in Septoria. The distribution of host families over the phylogenetic tree showed a highly dispersed pattern for 10 host plant families, providing new insight into the evolution of these fungi. It is concluded that trans-family host jumping is a major force driving the evolution of Septoria and Sphaerulina.
Taxonomic novelties: New genus - Caryophylloseptoria Verkley, Quaedvlieg & Crous; New species - Sphaerulina tirolensis Verkley, Quaedvlieg & Crous; New combinations - Caryophylloseptoria lychnidis (Desm.) Verkley, Quaedvlieg & Crous, Caryophylloseptoria silenes (Westend.) Verkley, Quaedvlieg & Crous, Caryophylloseptoria spergulae (Westend.) Verkley, Quaedvlieg & Crous, Sphaerulina aceris (Lib.) Verkley, Quaedvlieg & Crous, Sphaerulina cornicola (DC.: Fr.) Verkley, Quaedvlieg & Crous, Sphaerulina gei (Roberge ex Desm.) Verkley, Quaedvlieg & Crous, Sphaerulina hyperici (Roberge ex Desm.) Verkley, Quaedvlieg & Crous, Sphaerulina frondicola (Fr.) Verkley, Quaedvlieg & Crous, Sphaerulina socia (Pass.) Quaedvlieg, Verkley & Crous; Epitypifications (basionyms) - Ascochyta lysimachiae Lib., Septoria astragali Roberge ex Desm., Septoria cerastii Roberge ex Desm., Septoria clematidis Roberge ex Desm., Septoria cruciatae Roberge ex Desm., Septoria spergulae Westend., Septoria epilobii Westend., Septoria galeopsidis Westend., Septoria gei Roberge ex Desm., Septoria hyperici Roberge ex Desm., Septoria rubi Westend., Septoria senecionis Westend., Septoria urticae Roberge ex Desm.
Keywords: Evolution; Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST); Mycosphaerella; Mycosphaerellaceae; Phloeospora; Pleosporales; Septoria; Sphaerulina; host jumping; host specificity; new genus; new species; systematics; taxonomy.
Figures








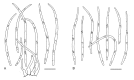














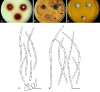


















Similar articles
-
Sizing up Septoria.Stud Mycol. 2013 Jun 30;75(1):307-90. doi: 10.3114/sim0017. Stud Mycol. 2013. PMID: 24014902 Free PMC article.
-
Redisposition of phoma-like anamorphs in Pleosporales.Stud Mycol. 2013 Jun 30;75(1):1-36. doi: 10.3114/sim0004. Stud Mycol. 2013. PMID: 24014897 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic lineages in Pseudocercospora.Stud Mycol. 2013 Jun 30;75(1):37-114. doi: 10.3114/sim0005. Stud Mycol. 2013. PMID: 24014898 Free PMC article.
-
Fusarium: more than a node or a foot-shaped basal cell.Stud Mycol. 2021 Aug 17;98:100116. doi: 10.1016/j.simyco.2021.100116. eCollection 2021 Apr. Stud Mycol. 2021. PMID: 34466168 Free PMC article.
-
Redisposition of acremonium-like fungi in Hypocreales.Stud Mycol. 2023 Jun;105:23-203. doi: 10.3114/sim.2023.105.02. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Stud Mycol. 2023. PMID: 38895703 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Fungal Assemblages in Different Habitats in an Erman's Birch Forest.Front Microbiol. 2016 Aug 30;7:1368. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01368. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27625646 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal Planet description sheets: 281-319.Persoonia. 2014 Dec;33:212-89. doi: 10.3767/003158514X685680. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Persoonia. 2014. PMID: 25737601 Free PMC article.
-
Wide Distribution of Teratosphaeria epicoccoides and T. destructans Associated with Diseased Eucalyptus Leaves in Plantations in Southern China.Microorganisms. 2024 Jan 9;12(1):129. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12010129. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38257956 Free PMC article.
-
Application of the consolidated species concept to Cercospora spp. from Iran.Persoonia. 2015 Jun;34:65-86. doi: 10.3767/003158515X685698. Epub 2014 Dec 1. Persoonia. 2015. PMID: 26240446 Free PMC article.
-
Polyketide-Derived Secondary Metabolites from a Dothideomycetes Fungus, Pseudopalawania siamensisgen. et sp. nov., (Muyocopronales) with Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activities.Biomolecules. 2020 Apr 8;10(4):569. doi: 10.3390/biom10040569. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32276418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrianova TV. (1987). Problems of classification and phylogeny of Septoria species. Mikologiya i Fitopatologiya 21: 393–399
-
- Aptroot A. (2006). Mycosphaerella and its anamorphs 2. Conspectus of Mycosphaerella. CBS Biodiversity Series 5 CBS-KNAW Fungal Biodiversity Centre, Utrecht, The Netherlands:
-
- Arx JA von. (1983). Mycosphaerella and its anamorphs. Proceedings Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen, Series C - Biological and Medical Sciences 86 (1): 15–54
-
- Beach WS. (1919). Biological spezialization in the genus Septoria. American Journal of Botany 6: 1–33
-
- Braun U. (1995). A monograph of Cercosporella, Ramularia and allied genera (Phytopathogenic Hyphomycetes). Vol. 1 IHW-Verlag, Eching:
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
