Effect of thiamine pyrophosphate on ischemia-reperfusion induced oxidative damage in rat kidney
- PMID: 24014907
- PMCID: PMC3757600
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.115005
Effect of thiamine pyrophosphate on ischemia-reperfusion induced oxidative damage in rat kidney
Abstract
Objectives: The biochemical effects of thiamine pyrophosphate on ischemia-reperfusion (IR) induced oxidative damage and DNA mutation in rat kidney tissue were investigated, and compared to thiamine.
Materials and methods: Rats were divided into four groups: renal ischemia-reperfusion (RIR); thiamine pyrophosphate + RIR (TPRIR); thiamine + RIR (TRIR); and sham group (SG).
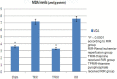
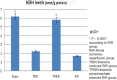
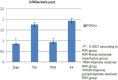
Results: The results of biochemical experiments have shown that malondialdehyde (MDA) levels in rat kidney tissue after TRIR and TPRIR treatment were 7.2 ± 0.5 (P > 0.05) and 3.3 ± 0.3 (P < 0.0001) μmol/g protein, respectively. The MDA levels in the SG rat kidney tissue and in RIR group were 3.6 ± 0.2 (P < 0.0001) and 7.6 ± 0.6 μmol/g protein, respectively. Total glutathione (tGSH) levels in TRIR, TPRIR, SG, and RIR animal groups were 2.2 ± 0.3 (P > 0.05), 5.8 ± 0.4 (P < 0.0001), 6.2 ± 0.2 (P < 0.0001), and 1.7 ± 0.2 nmol/g protein, respectively. In the TRIR, TPRIR, SG, and RIR animal groups; 8-hydroxyguanine (8-OHGua)/Gua levels, which indicate mutagenic DNA, were 1.75 ± 0.12 (P > 0.05), 0.93 ± 0.1 (P < 0.0001), 0.85 ± 0.08 (P < 0.0001), and 1.93 ± 0.24 pmol/L, respectively.
Conclusions: It has been shown that thiamine pyrophosphate prevents increase in mutagenic DNA in IR induced oxidative damage, whereas thiamine does not have this effect.
Keywords: DNA mutation; ischemia-reperfusion; oxidative damage; rat; thiamine pyrophosphate.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparative investigation of biochemical and histopathological effects of thiamine and thiamine pyrophosphate on ischemia-reperfusion induced oxidative damage in rat ovarian tissue.Arch Pharm Res. 2013 Sep;36(9):1133-9. doi: 10.1007/s12272-013-0173-8. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Arch Pharm Res. 2013. PMID: 23760618
-
The effect of thiamine pyrophosphate on ethambutol-induced ocular toxicity.Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2016 Sep;35(3):222-7. doi: 10.3109/15569527.2015.1077857. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26339826
-
The effects of thiamine pyrophosphate on ethanol induced optic nerve damage.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019 Jul 5;20(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s40360-019-0319-5. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31277705 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of nimesulide on oxidative damage inflicted by ischemia-reperfusion on the rat renal tissue.Ren Fail. 2015 Mar;37(2):323-31. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2014.985996. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Ren Fail. 2015. PMID: 25418059
-
Use of thiamine pyrophosphate to prevent infertility developing in rats undergoing unilateral ovariectomy and with ischemia reperfusion induced in the contralateral ovary.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2013 Oct;170(2):521-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2013.07.027. Epub 2013 Aug 3. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2013. PMID: 23916585
Cited by
-
Alterations in Gut Vitamin and Amino Acid Metabolism are Associated with Symptoms and Neurodevelopment in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder.J Autism Dev Disord. 2022 Jul;52(7):3116-3128. doi: 10.1007/s10803-021-05066-w. Epub 2021 Jul 14. J Autism Dev Disord. 2022. PMID: 34263410 Free PMC article.
-
The adaptive regulation of thiamine pyrophosphokinase-1 facilitates malignant growth during supplemental thiamine conditions.Oncotarget. 2018 Oct 23;9(83):35422-35438. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26259. eCollection 2018 Oct 23. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30459934 Free PMC article.
-
Acacetin Attenuates Renal Damage-Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion with Declining Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress in Mice.Int J Prev Med. 2020 Feb 17;11:22. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_512_18. eCollection 2020. Int J Prev Med. 2020. PMID: 32175062 Free PMC article.
-
Thiamine pyrophosphate may protect indomethacin-induced small intestinal enteropathy in rats by inhibiting intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 29. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04213-9. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40299020
-
Interplay Between Thiamine and p53/p21 Axes Affects Antiproliferative Action of Cisplatin in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells by Changing Metabolism of 2-Oxoglutarate/Glutamate.Front Genet. 2021 Apr 1;12:658446. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.658446. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33868388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Křen V, Walterová D. Silybin and silymarin—new effects and applications. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2005;149:29–41. - PubMed
-
- Lindsay TF, Liauw S, Romaschin AD, Walker PM. The effect of ischemia/reperfusion on adenine nucleotide metabolism and xanthine oxidase production in skeletal muscle. J Vasc Surg. 1990;12:8–15. - PubMed
-
- McCord JM. Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischemic tissue injury. N Engl J Med. 1985;312:159–63. - PubMed
-
- Del Maestro RF. An approach to free radicals in medicine and biology. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1980;492:153–68. - PubMed
-
- Marnett LJ. Oxyradicals and DNA damage. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:361–70. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

