A case of thrombocytopenia caused by rifampicin and pyrazinamide
- PMID: 24014922
- PMCID: PMC3757615
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.114998
A case of thrombocytopenia caused by rifampicin and pyrazinamide
Abstract
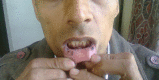
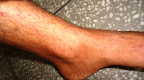
A 32-year-old male patient was diagnosed as having pulmonary tuberculosis and put on category II antitubercular regime since he had a history of antituberculosis treatment 10 years ago. Within 3 weeks, patient presented with ulcers in mouth, and blood picture confirmed thrombocytopenia. Rifampicin-induced thrombocytopenia was suspected and antitubercular treatment stopped. Patient improved and was re-exposed to the drugs one by one. After re-exposure with pyrazinamide, the platelet count decreased drastically and oral mucosal ecchymoses reappeared, while with rifampicin, thrombocytopenia was accompanied with petechiae on legs and forearms. Isoniazid, ethambutol, and streptomycin were continued.
Keywords: Antituberculosis treatment; ecchymoses; petechiae; thrombocytopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- The use of the WHO-UMC system for standardized case causality assessment. [Last accessed on 2012 Sep 30]. Accessed from: http://www.WHO-UMC.org/graphics/4409.pdf .
-
- Naranjo CA, Busto U, Sellers EM, Sandor P, Ruiz I, Roberts EA, et al. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin Pharacol Ther. 1981;30:239–45. - PubMed
-
- Vipan WH. Quinine a cause of purpura. Lancet. 1865;2:37.
-
- Bassi L, Perna G, Silvestri LG. Antibodies against rifampicin in patients with tuberculosis after discontinuation of daily treatment. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976;114:1189–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources