Early experience of pre- and post-contrast 7.0T MRI in brain tumors
- PMID: 24015044
- PMCID: PMC3763113
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.9.1362
Early experience of pre- and post-contrast 7.0T MRI in brain tumors
Abstract
We investigated the safety and clinical applicability of 7.0 Tesla (T) brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in patients with brain tumors. Twenty-four patients with intraaxial or extraaxial brain tumors were enrolled in this study. 7.0T MRIs of T2*-weighted axial and T1-weighted coronal or sagittal images were obtained and compared with 1.5T brain MRIs. The T2*-weighted images from 7.0T brain MRI revealed detailed microvasculature and the internal contents of supratentorial brain tumors better than that of 1.5T brain MRI. For brain tumors located in parasellar areas or areas adjacent to major cerebral vessels, flow-related artifacts were exaggerated in the 7.0T brain MRIs. For brain tumors adjacent to the skull base, susceptibility artifacts in the interfacing areas of the paranasal sinus and skull base hampered the aquisition of detailed images and information on brain tumors in the 7.0T brain MRIs. This study shows that 7.0T brain MRI can provide detailed information on the intratumoral components and margins in supratentorial brain tumors. Further studies are needed to develop refined MRI protocols for better images of brain tumors located in the skull base, parasellar, and adjacent major cerebrovascular structures.
Keywords: 7.0 Tesla; Brain Neoplasms; Clinical Applicability; Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Safety.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


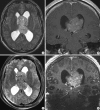
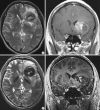


References
-
- Van der Kolk AG, Hendrikse J, Zwanenburg JJ, Visser F, Luijten PR. Clinical applications of 7 T MRI in the brain. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82:708–718. - PubMed
-
- Moenninghoff C, Maderwald S, Theysohn JM, Kraff O, Ladd ME, El Hindy N, van de Nes J, Forsting M, Wanke I. Imaging of adult astrocytic brain tumours with 7 T MRI: preliminary results. Eur Radiol. 2010;20:704–713. - PubMed
-
- Pinker K, Noebauer-Huhmann IM, Stavrou I, Hoeftberger R, Szomolanyi P, Weber M, Stadlbauer A, Grabner G, Knosp E, Trattnig S. High-field, high-resolution, susceptibility-weighted magnetic resonance imaging: improved image quality by addition of contrast agent and higher field strength in patients with brain tumors. Neuroradiology. 2008;50:9–16. - PubMed
-
- Strzhizhovskĭ AD, Galaktionova GV. Proliferation of bone marrow cells upon exposure to constant magnetic fields of ultra-high strength. Tsitologiia. 1978;20:717–720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

