Stable Formation of Fruiting Body in Cordyceps bassiana
- PMID: 24015103
- PMCID: PMC3763178
- DOI: 10.4489/MYCO.2007.35.4.230
Stable Formation of Fruiting Body in Cordyceps bassiana
Abstract
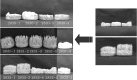
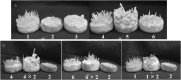
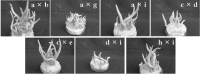
In order to breed a Cordyceps bassiana isolate that stably forms fruiting body in artificial cultivation, isolates derived from subculturing and single spores were tested through mating. From C. bassiana EFCC 783, three subcultured isolates EFCC 2830, EFCC 2831 and EFCC 2832 were obtained and fourteen single conidial isolates were obtained from these three subcultured isolates. Two different morphological types were found in the fourteen single conidial isolates. One type was able to form synnemata and another type was not able to form synnemata. Since switch of morphological type was not observed despite their continuous subculturing, cross was performed between the two types and the formation of fruiting body was examined. Ascospores were obtained from a selected fruiting body formed by hybrid of the cross. Self-cross and combinational cross of the ascospore-derived isolates generated hybrids that stably produce high quality fruiting body in artificial media.
Keywords: Cordyceps bassiana; Mating type; Perithecial fruiting bodies; Single conidial isolates; Synnemata.
Figures


References
-
- Dodge BO. The life history of Ascobolus magnificus: Origin of ascocarp from two strains. Mycologia. 1920;12:115–134.
-
- Edgerton CW. Plus and minus strains in the genus Glomerella. Am J Bot. 1914;1:244–254.
-
- Humber RA. Fungal pathogens and parasites of insects. In: Priest FG, Goodfellow M, editors. Applied Microbial Systematics. Dordrecht: Kluwer Acadenic Publishers; 2000. pp. 203–230.
-
- Kobayasi Y. The genus Cordyceps and its allies. Sci Rept Tokyo Bunrika Daigaku Sect B. 1941;5:53–260.
-
- Kobayasi Y, Shimizu D. Cordyceps species from Japan, 6. Bull Nat Sci Mus. 1983;9:15.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
