Chaperones of the endoplasmic reticulum are required for Ve1-mediated resistance to Verticillium
- PMID: 24015989
- PMCID: PMC6638731
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12071
Chaperones of the endoplasmic reticulum are required for Ve1-mediated resistance to Verticillium
Abstract
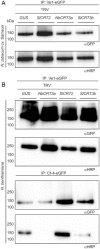
The tomato receptor-like protein (RLP) Ve1 mediates resistance to the vascular fungal pathogen Verticillium dahliae. To identify the proteins required for Ve1 function, we transiently expressed and immunopurified functional Ve1-enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) from Nicotiana benthamiana leaves, followed by mass spectrometry. This resulted in the identification of peptides originating from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident chaperones HSP70 binding proteins (BiPs) and a lectin-type calreticulin (CRT). Knock-down of the different BiPs and CRTs in tomato resulted in compromised Ve1-mediated resistance to V. dahliae in most cases, showing that these chaperones play an important role in Ve1 functionality. Recently, it has been shown that one particular CRT is required for the biogenesis of the RLP-type Cladosporium fulvum resistance protein Cf-4 of tomato, as silencing of CRT3a resulted in a reduced pool of complex glycosylated Cf-4 protein. In contrast, knock-down of the various CRTs in N. benthamiana or N. tabacum did not result in reduced accumulation of mature complex glycosylated Ve1 protein. Together, this study shows that the BiP and CRT ER chaperones differentially contribute to Cf-4- and Ve1-mediated immunity.
© 2013 BSPP AND JOHN WILEY & SONS LTD.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Endoplasmic reticulum-quality control chaperones facilitate the biogenesis of Cf receptor-like proteins involved in pathogen resistance of tomato.Plant Physiol. 2012 Aug;159(4):1819-33. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.196741. Epub 2012 May 30. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22649272 Free PMC article.
-
Interfamily transfer of tomato Ve1 mediates Verticillium resistance in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2011 Aug;156(4):2255-65. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.180067. Epub 2011 May 26. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21617027 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of the tomato immune receptor Ve1 through domain swaps with its non-functional homolog Ve2.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 5;9(2):e88208. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088208. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24505431 Free PMC article.
-
Tomato Ve-resistance locus: resilience in the face of adversity?Planta. 2021 Nov 22;254(6):126. doi: 10.1007/s00425-021-03783-1. Planta. 2021. PMID: 34811576 Review.
-
Chaperones and foldases in endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling in plants.Plant Signal Behav. 2011 Feb;6(2):232-6. doi: 10.4161/psb.6.2.15490. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Plant Signal Behav. 2011. PMID: 21427533 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Different Gene Expressions of Resistant and Susceptible Hop Cultivars in Response to Infection with a Highly Aggressive Strain of Verticillium albo-atrum.Plant Mol Biol Report. 2015;33(3):689-704. doi: 10.1007/s11105-014-0767-4. Plant Mol Biol Report. 2015. PMID: 25999664 Free PMC article.
-
ER-mediated control for abundance, quality, and signaling of transmembrane immune receptors in plants.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Feb 25;5:65. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00065. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24616730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ER quality control components UGGT and STT3a are required for activation of defense responses in bir1-1.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 16;10(3):e0120245. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120245. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25775181 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-level genome assembly of Mentha longifolia L. reveals gene organization underlying disease resistance and essential oil traits.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Jul 29;12(8):jkac112. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac112. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35551385 Free PMC article.
-
When supply does not meet demand-ER stress and plant programmed cell death.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Jun 4;5:211. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00211. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24926295 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beck, M. , Heard, W. , Mbengue, M. and Robatzek, S. (2012) The INs and OUTs of pattern recognition receptors at the cell surface. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 15, 367–374. - PubMed
-
- Belfanti, E. , Silfverberg‐Dilworth, E. , Tartarini, S. , Patocchi, A. , Barbieri, M. , Zhu, J. , Vinatzer, B.A. , Gianfranceschi, L. , Gessler, C. and Sansavini, S. (2004) The HcrVf2 gene from a wild apple confers scab resistance to a transgenic cultivated variety. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 101, 886–890. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boller, T. and Felix, G. (2009) A renaissance of elicitors: perception of microbe‐associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern‐recognition receptors. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 60, 379–407. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

