Treatment strategies in patients with statin intolerance: the Cleveland Clinic experience
- PMID: 24016512
- PMCID: PMC4038261
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ahj.2013.06.004
Treatment strategies in patients with statin intolerance: the Cleveland Clinic experience
Abstract
Background: Statin therapy is a proven effective treatment of hyperlipidemia. However, a significant number of patients cannot tolerate statins. This study was conducted to review treatment strategies for patients intolerant to statin therapy with a focus on intermittent statin dosing.
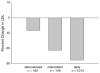
Methods and results: We performed a retrospective analysis of medical records of 1,605 patients referred to the Cleveland Clinic Preventive Cardiology Section for statin intolerance between January 1995 and March 2010 with at least a 6-month follow-up. The changes in lipid profile, achievement of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) goals, and statin tolerance rate were analyzed. Most (72.5%) of patients with prior statin intolerance were able to tolerate a statin for the median follow-up time of 31 months. Patients on intermittent statin dosing (n = 149) had significantly lower LDL-C reduction compared with daily dosing group (n = 1,014; 21.3% ± 4.0% vs 27.7% ± 1.4%, P < .04). However, compared with the statin discontinued group (n = 442), they had a significantly higher LDL-C reduction (21.3% ± 4.0% vs 8.3 ± 2.2%, P < .001), and a significantly higher portion achieved their Adult Treatment Panel III goal of LDL-C (61% vs 44%, P < .05). There was a trend toward a decrease in all-cause mortality at 8 years for patients on daily and intermittent statin dosing compared with those who discontinued statin (P = .08).
Conclusions: Most patients with previous statin intolerance can tolerate subsequent trial of statin. A strategy of intermittent statin dosing can be an effective therapeutic option in some patients and may result in reduction in LDL-C and achievement of LDL-C goals.
© 2013.
References
-
- Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Merz CN, Brewer HB, Jr, Clark LT, Hunninghake DB, Pasternak RC, Smith SC, Jr, Stone NJ. Implications of recent clinical trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:720–732. - PubMed
-
- Cheng AY, Leiter LA. Implications of recent clinical trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2006;21:400–404. - PubMed
-
- Davidson MH, Robinson JG. Safety of aggressive lipid management. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;49:1753–1762. - PubMed
-
- Kashani A, Phillips CO, Foody JM, Wang Y, Mangalmurti S, Ko DT, et al. Risks associated with statin therapy: a systematic overview of randomized clinical trials. Circulation. 2006;114:2788–97. - PubMed
-
- Gomez Sandoval YH, Braganza MV, Daskalopoulou SS. Statin discontinuation in high-risk patients: a systematic review of the evidence. Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17:3669–89. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical