Investigation of the factors associated with circulating soluble CD36 levels in patients with HCV-related chronic liver disease
- PMID: 24016701
- PMCID: PMC3846866
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-5996-5-51
Investigation of the factors associated with circulating soluble CD36 levels in patients with HCV-related chronic liver disease
Abstract
Background: CD36, a class B scavenger receptor, participates in the pathogenesis of metabolic dysregulation such as insulin resistance, hepatic steatosis, and atherosclerosis. Persistent hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection often evokes these metabolic abnormalities. The primary purpose of this study was to investigate the role of CD36 in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis caused by chronic HCV infection.
Methods: Forty-five patients with HCV-related chronic liver disease (CLD-C) were enrolled in this study. CD36 expression in the liver specimen was examined by an immunohistochemical procedure. The concentrations of circulating soluble form of CD36 (sCD36) and oxLDL were determined by the enzyme-linked innunosorbent assay. Insulin resistance was estimated by the values of HOMA-IR.
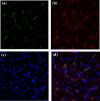
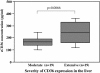
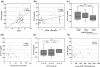
Results: Moderate to extensive hepatic CD36 expression was observed in the sinusoids of all enrolled CLD-C patients. CD36-positive sinusoids appeared to be identical to Kupffer cells. The severity of CD36 expression in the hepatic sinusoids was significantly correlated with the sCD36 level in sera of patients with CLD-C. The serum sCD36 levels were significantly correlated with body mass index and serum oxLDL levels in those patients. However, the serum sCD36 concentrations were independent of the values of HOMA-IR and the severity of hepatic steatosis.
Conclusions: These data suggest that the serum sCD36 levels reflect the severity of CD36 expression on the Kupffer cells in patients with CLD-C, and that the serum sCD36 levels were associated with obesity, although the levels were independent of insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in those patients.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Increased soluble CD36 is linked to advanced steatosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Eur J Clin Invest. 2014 Jan;44(1):65-73. doi: 10.1111/eci.12192. Epub 2013 Nov 23. Eur J Clin Invest. 2014. PMID: 24134687
-
Exacerbation of insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis deriving from zinc deficiency in patients with HCV-related chronic liver disease.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2015 Feb;163(1-2):81-8. doi: 10.1007/s12011-014-0177-3. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2015. PMID: 25413880 Clinical Trial.
-
High sCD36 plasma level is associated with steatosis and its severity in patients with genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C.J Viral Hepat. 2013 Mar;20(3):174-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2012.01641.x. Epub 2012 Jul 9. J Viral Hepat. 2013. PMID: 23383656
-
Soluble CD36- a marker of the (pathophysiological) role of CD36 in the metabolic syndrome?Arch Physiol Biochem. 2011 May;117(2):57-63. doi: 10.3109/13813455.2010.543136. Epub 2011 Jan 21. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21250778 Review.
-
Understanding lipotoxicity in NAFLD pathogenesis: is CD36 a key driver?Cell Death Dis. 2020 Sep 25;11(9):802. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03003-w. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32978374 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating CD36 and oxLDL levels are associated with cardiovascular risk factors in young subjects.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2014 Apr 28;14:54. doi: 10.1186/1471-2261-14-54. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2014. PMID: 24766787 Free PMC article.
-
CD36 is a co-receptor for hepatitis C virus E1 protein attachment.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 22;6:21808. doi: 10.1038/srep21808. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26898231 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble cluster of differentiation 36 concentrations are not associated with cardiovascular risk factors in middle-aged subjects.Biomed Rep. 2016 May;4(5):642-648. doi: 10.3892/br.2016.622. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Biomed Rep. 2016. PMID: 27123261 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating soluble CD36 as a novel biomarker for progression and prognosis of HBV-related liver diseases.Front Microbiol. 2022 Nov 2;13:1039614. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1039614. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36406414 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating CD36 is increased in hyperlipidemic mice: Cellular sources and triggers of release.Free Radic Biol Med. 2021 May 20;168:180-188. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.03.004. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33775772 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Negro F, Sanyal AJ. Hepatitis C virus, steatosis and lipid abnormalities: clinical and pathologic data. Liver Int. 2009;S2:26–37. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

