Impact of azithromycin treatment on macrophage gene expression in subjects with cystic fibrosis
- PMID: 24018177
- PMCID: PMC4376357
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcf.2013.08.007
Impact of azithromycin treatment on macrophage gene expression in subjects with cystic fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Azithromycin treatment improves clinical parameters in patients with CF, and alters macrophage activation from a pro-inflammatory (M1) phenotype to a pro-fibrotic, alternatively activated (M2) phenotype. The transcriptional profile of cells from patients receiving azithromycin is unknown.
Methods: Gene expression in association with macrophage polarization, inflammation, and tissue remodeling was assessed from sputum samples collected from patients with CF. Transcriptional profiles and clinical characteristics, including azithromycin therapy, were compared.
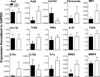
Results: Expression of NOS2 and TNFα was decreased in subjects receiving azithromycin, whereas expression of M2-associated genes was unaffected. Principal component analysis revealed gene expression profiles consistent with M1- (MMP9, NOS2, and TLR4) or M2-polarization (CCL18, fibronectin, and MR1) in select subject groups. These expression signatures did not significantly correlate with clinical characteristics.
Conclusions: Pro-inflammatory gene expression was low in subjects receiving AZM. Genes were stratified into groupings characteristic of M1- or M2-polarization, suggesting that overall polarization status is distinct among patient groups.
Keywords: Azithromycin; Cystic fibrosis; Macrophage phenotype.
© 2013.
Figures

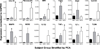
References
-
- Gibson RL, Burns JL, Ramsey BW. Pathophysiology and management of pulmonary infections in cystic fibrosis. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 2003 Oct 15;168(8):918–951. - PubMed
-
- McKeon DJ, Cadwallader KA, Idris S, et al. Cystic fibrosis neutrophils have normal intrinsic reactive oxygen species generation. Eur Respir J. Jun;35(6):1264–1272. - PubMed
-
- Equi A, Balfour-Lynn IM, Bush A, Rosenthal M. Long term azithromycin in children with cystic fibrosis: a randomised, placebo-controlled crossover trial. Lancet. 2002 Sep 28;360(9338):978–984. - PubMed
-
- Saiman L, Anstead M, Mayer-Hamblett N, et al. Effect of azithromycin on pulmonary function in patients with cystic fibrosis uninfected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a randomized controlled trial. Jama. May 5;303(17):1707–1715. - PubMed
-
- Saiman L, Marshall BC, Mayer-Hamblett N, et al. Azithromycin in patients with cystic fibrosis chronically infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a randomized controlled trial. Jama. 2003 Oct 1;290(13):1749–1756. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

