Inactivation of tumor-specific CD8⁺ CTLs by tumor-infiltrating tolerogenic dendritic cells
- PMID: 24018532
- PMCID: PMC3806489
- DOI: 10.1038/icb.2013.38
Inactivation of tumor-specific CD8⁺ CTLs by tumor-infiltrating tolerogenic dendritic cells
Erratum in
- Immunol Cell Biol. 2013 Nov-Dec;91(10):665
Abstract
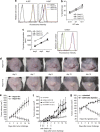
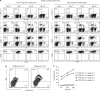
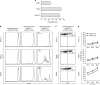
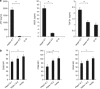
Cancer immunosurveillance failure is largely attributed to the insufficient activation of tumor-specific class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecule (MHC-I)-restricted CD8⁺ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). DEC-205⁺ dendritic cells (DCs), having the ability to cross-present, can present captured tumor antigens on MHC-I alongside costimulatory molecules, inducing the priming and activation of tumor-specific CD8⁺ CTLs. It has been suggested that reduced levels of costimulatory molecules on DCs may be a cause of impaired CTL induction and that some tumors may induce the downregulation of costimulatory molecules on tolerogenic DCs. To examine such possibilities, we established two distinct types of murine hepatoma cell lines, named Hepa1-6-1 and Hepa1-6-2 (derived from Hepa1-6 cells), and confirmed that they display similar antigenicities, as well as identical surface expression of MHC-I. We found that Hepa1-6-1 had the ability to grow continuously after subcutaneous implantation into syngeneic C57BL/6 mice and did not prime CD8⁺ CTLs. In contrast, Hepa1-6-2 cells, which display reduced levels of adhesion molecules, such as Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1 (ICAM-1), failed to grow in vivo and efficiently primed CTLs. Moreover, Hepa1-6-1-derived factors, such as transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and α-fetoprotein (AFP), converted CD11c(high) MHC-II(high) DEC-205⁺ DC subsets into tolerogenic cells, displaying downregulated costimulatory molecules and having impaired cross-presenting capacities. These immunosuppressive tolerogenic DCs appeared to inhibit the induction of tumor-specific CD8⁺ CTLs and suppress their cytotoxic functions within the tumor. Together, the findings presented here provide a new method of cancer immunotherapy using the selective suppression, depletion or alteration of immunosuppressive tolerogenic DCs within tumors.
Figures

References
-
- Zinkernagel RM, Doherty PC. Restriction of in vitro T cell-mediated cytotoxicity in lymphocytic choriomeningitis within a syngeneic or semiallogeneic system. Nature. 1974;248:701–702. - PubMed
-
- Tsang KY, Zhu M, Even J, Gulley J, Arlen P, Schlom J. The infection of human dendritic cells with recombinant avipox vectors expressing a costimulatory molecule transgene (CD80) to enhance the activation of antigen-specific cytolytic T cells. Cancer Res. 2001;61:7568–7576. - PubMed
-
- Germain RN. MHC-dependent antigen processing and peptide presentation: providing ligands for T lymphocyte activation. Cell. 1994;76:287–299. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi H. Antigen processing and presentation. Microbiol Immunol. 1993;37:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

