Retinal angiogenesis suppression through small molecule activation of p53
- PMID: 24018558
- PMCID: PMC3784529
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI67315
Retinal angiogenesis suppression through small molecule activation of p53
Abstract
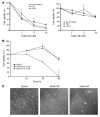
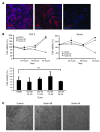
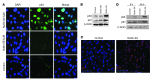
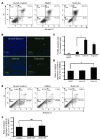
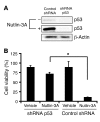
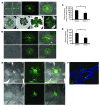
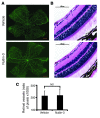
Neovascular age-related macular degeneration is a leading cause of irreversible vision loss in the Western world. Cytokine-targeted therapies (such as anti-vascular endothelial growth factor) are effective in treating pathologic ocular angiogenesis, but have not led to a durable effect and often require indefinite treatment. Here, we show that Nutlin-3, a small molecule antagonist of the E3 ubiquitin protein ligase MDM2, inhibited angiogenesis in several model systems. We found that a functional p53 pathway was essential for Nutlin-3-mediated retinal antiangiogenesis and disruption of the p53 transcriptional network abolished the antiangiogenic activity of Nutlin-3. Nutlin-3 did not inhibit established, mature blood vessels in the adult mouse retina, suggesting that only proliferating retinal vessels are sensitive to Nutlin-3. Furthermore, Nutlin-3 inhibited angiogenesis in nonretinal models such as the hind limb ischemia model. Our work demonstrates that Nutlin-3 functions through an antiproliferative pathway with conceivable advantages over existing cytokine-targeted antiangiogenesis therapies.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ilimaquinone inhibits neovascular age-related macular degeneration through modulation of Wnt/β-catenin and p53 pathways.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Nov;161:105146. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105146. Epub 2020 Aug 16. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32814173
-
Antiangiogenic activity of the MDM2 antagonist nutlin-3.Circ Res. 2007 Jan 5;100(1):61-9. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000253975.76198.ff. Epub 2006 Nov 30. Circ Res. 2007. PMID: 17138942
-
Effect of MDM2 and vascular endothelial growth factor inhibition on tumor angiogenesis and metastasis in neuroblastoma.Angiogenesis. 2011 Sep;14(3):255-66. doi: 10.1007/s10456-011-9210-8. Epub 2011 Apr 12. Angiogenesis. 2011. PMID: 21484514
-
Effects of MDM2 inhibitors on vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated tumor angiogenesis in human breast cancer.Angiogenesis. 2014 Jan;17(1):37-50. doi: 10.1007/s10456-013-9376-3. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Angiogenesis. 2014. PMID: 23907365
-
Nanoparticles loaded with Nutlin-3 display cytotoxicity towards p53(wild-type) JVM-2 but not towards p53(mutated) BJAB leukemic cells.Curr Med Chem. 2013;20(21):2712-22. doi: 10.2174/0929867311320210007. Curr Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23627936 Review.
Cited by
-
Antiangiogenic Therapeutic Potential of Peptides Derived from the Molecular Motor KIF13B that Transports VEGFR2 to Plasmalemma in Endothelial Cells.Am J Pathol. 2017 Jan;187(1):214-224. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.09.010. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Am J Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27863212 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the immunomodulatory dance: endothelial cells' function and their role in non-small cell lung cancer.Mol Cancer. 2025 Jan 16;24(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02221-6. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39819502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A small molecule p53 activator attenuates Fanconi anemia leukemic stem cell proliferation.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 May 22;9(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0882-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29784053 Free PMC article.
-
The MDM2-p53 axis regulates norrin/frizzled4 signaling and blood-CNS barrier function.Sci Signal. 2025 Jul 8;18(894):eadt0983. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.adt0983. Epub 2025 Jul 8. Sci Signal. 2025. PMID: 40627684 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor suppressor protein p53 negatively regulates ischemia-induced angiogenesis and arteriogenesis.J Vasc Surg. 2018 Dec;68(6S):222S-233S.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2018.02.055. Epub 2018 Aug 17. J Vasc Surg. 2018. PMID: 30126780 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

