Botulinum toxin for masseter hypertrophy
- PMID: 24018587
- PMCID: PMC7207780
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007510.pub3
Botulinum toxin for masseter hypertrophy
Abstract
Background: Benign masseter muscle hypertrophy is an uncommon clinical phenomenon of uncertain aetiology which is characterised by a soft swelling near the angle of the mandible. The swelling may on occasion be associated with facial pain and can be prominent enough to be considered cosmetically disfiguring. Varying degrees of success have been reported for some of the treatment options for masseter hypertrophy, which range from simple pharmacotherapy to more invasive surgical reduction. Injection of botulinum toxin type A into the masseter muscle is generally considered a less invasive modality and has been advocated for cosmetic sculpting of the lower face. Botulinum toxin type A is a powerful neurotoxin which is produced by the anaerobic organism Clostridium botulinum and when injected into a muscle causes interference with the neurotransmitter mechanism producing selective paralysis and subsequent atrophy of the muscle.This review is an update of a previously published Cochrane review.
Objectives: To assess the efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin type A compared to placebo or no treatment, for the management of benign bilateral masseter hypertrophy.
Search methods: We searched the following databases from inception to April 2013: the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL); MEDLINE (via PubMed); EMBASE (via embase.com); Web of Science; CINAHL; Academic Search Premier (via EBSCOhost); ScienceDirect; LILACS (via BIREME); PubMed Central and Google Scholar (from 1700 to 19 April 2013). We searched two bibliographic databases of regional journals (IndMED and Iranmedex) which were expected to contain relevant trials. We also searched reference lists of relevant articles and contacted investigators to identify additional published and unpublished studies.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and controlled clinical trials (CCTs) comparing intra-masseteric injections of botulinum toxin versus placebo administered for cosmetic facial sculpting in individuals of any age with bilateral benign masseter hypertrophy, which had been self-evaluated and confirmed by clinical and radiological examination were considered for inclusion. We excluded participants with unilateral or compensatory contralateral masseter hypertrophy resulting from head and neck radiotherapy.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently screened the search results. For future updates, two authors will independently extract data and assess trial quality using the Cochrane risk of bias tool. Risk ratios (RR) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) will be calculated for all dichotomous outcomes and the mean difference (MD) and 95% CI will be calculated for continuous outcomes.
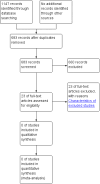
Main results: We retrieved 683 unique references to studies. After screening these references 660 were excluded for being non-applicable. We assessed 23 full text articles for eligibility and all of these studies were excluded from the review.
Authors' conclusions: We were unable to identify any RCTs or CCTs assessing the efficacy and safety of intra-masseteric injections of botulinum toxin for people with bilateral benign masseter hypertrophy. The absence of high level evidence for the effectiveness of this intervention emphasises the need for well-designed, adequately powered RCTs.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no financial conflicts of interest and the authors declare that they do not have any associations with any parties who may have vested interests in the results of this review.
Update of
-
Botulinum toxin for masseter hypertrophy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Jan 21;(1):CD007510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007510.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Sep 09;(9):CD007510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007510.pub3. PMID: 19160335 Updated.
References
References to studies excluded from this review
Ahn 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ahn KY, Kim ST. The change of maximum bite force after botulinum toxin type a injection for treating masseteric hypertrophy. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 2007;120(6):1662‐6. - PubMed
Bhogal 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bhogal PS, Hutton A, Monaghan A. A review of the current uses of Botox for dentally‐related procedures. Dental Update 2006;33(3):165‐8. - PubMed
Castro 2005 {published data only}
-
- Castro WH, Gomez RS, Silva Oliveira J, Moura MD, Gomez RS. Botulinum toxin type A in the management of masseter muscle hypertrophy. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2005;63(1):20‐4. - PubMed
Chikani 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chikhani L, Dichamp J. Bruxism, temporo‐mandibular dysfunction and botulinum toxin. Annales de Réadaptation et de Médecine Physique 2003;46(6):333‐7. - PubMed
Choe 2005 {published data only}
-
- Choe SW, Cho WI, Lee CK, Seo SJ. Effects of botulinum toxin type A on contouring of the lower face. Dermatologic Surgery 2005;31(5):502‐7. - PubMed
Collier 2009 {published data only}
-
- Collier J, Zou L. Quantitative measurement of the response of masseteric hypertrophy to treatment with botulinum toxin type‐A. British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2009;47(7):e30.
Hui 2002 {published data only}
-
- Hui AC. Botulinum toxin for treatment of masseteric hypertrophy. Journal of Neurology 2002;249(3):345. - PubMed
Işeri 2004 {published data only}
-
- Işeri M, Işeri PK. Treatment of unilateral masseter hypertrophy with botulinum toxin in two cases. Kulak Burun Boğaz Ihtisas Dergisi 2004;12(3‐4):99‐102. - PubMed
Jin 2010 {published data only}
-
- Jin SP, Cho S, Youn C, Feneran A, Haw S, Bak H, et al. Effectiveness of botulinum toxin type A and B in benign masseteric hypertrophy. Journal of Dermatology 2010;37(Suppl 1):78.
Kane 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kane MA. Botulinum toxin A for lower facial contouring: A prospective study. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery 2007;31(5):452‐3. - PubMed
Kaynar 1997 {published data only}
-
- Kaynar A, Parman Y, Poyanl A, Demirkol O, Birinci SH, Minareci O, et al. Therapeutic use of botulinum toxin in the treatment of masseter hypertrophy. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 1997;26(Suppl 1):116.
Kim 2003 {published data only}
-
- Kim HJ, Yum KW, Lee SS, Heo MS, Seo K. Effects of botulinum toxin type A on bilateral masseteric hypertrophy evaluated with computed tomographic measurement. Dermatologic Surgery 2003;29(5):484‐9. - PubMed
Lee 2007 {published data only}
-
- Lee CJ, Kim SG, Kim YJ, Han JY, Choi SH, Lee SI. Electrophysiologic change and facial contour following botulinum toxin A. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 2007;120(3):769‐78. - PubMed
Mischkowski 2005 {published data only}
-
- Mischkowski RA, Siessegger M, Lazar F, Zöller JE. Chemodenervation with botulinum toxin in masseteric hypertrophy. Mund‐, Kiefer‐ und Gesichtschirurgie 2005;9(2):101‐8. - PubMed
Moore 1994 {published data only}
-
- Moore AP, Wood GD. The medical management of masseteric hypertrophy with botulinum toxin type A. British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 1994;32(1):26‐8. - PubMed
Niamtu 1999 {published data only}
-
- Niamtu J. Aesthetic uses of botulinum toxin A. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 1999;57(10):1228‐33. - PubMed
Park 2003 {published data only}
-
- Park MY, Ahn KY, Jung DS. Botulinum toxin type A treatment for contouring of the lower face. Dermatologic Surgery 2003;29(5):477‐83. - PubMed
Rogers 1995 {published data only}
-
- Rogers BA, Whear NM. Medical management of masseteric hypertrophy. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 1995;53(4):492. - PubMed
Smyth 1994 {published data only}
-
- Smyth AG. Botulinum toxin treatment of bilateral masseteric hypertrophy. British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 1994;32(1):29‐33. - PubMed
To 2001 {published data only}
-
- To EW, Ahuja AT, Ho WS, King WW, Wong WK, Pang PC, et al. A prospective study of the effect of botulinum toxin A on masseteric muscle hypertrophy with ultrasonographic and electromyographic measurement. British Journal of Plastic Surgery 2001;54(3):197‐200. - PubMed
von Lindern 2001 {published data only}
-
- Lindern JJ, Niederhagen B, Appel T, Bergé S, Reich RH. Type A botulinum toxin for the treatment of hypertrophy of the masseter and temporal muscles: an alternative treatment. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 2001;107(2):327‐32. - PubMed
von Lindern 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lindern JJ, Niederhagen B, Bergé S, Appel T. Type A botulinum toxin in the treatment of chronic facial pain associated with masticatory hyperactivity. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2003;61(7):774‐8. - PubMed
Yu 2007 {published data only}
-
- Yu CC, Chen PK, Chen YR. Botulinum toxin a for lower facial contouring: a prospective study. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery 2007;31(5):445‐51. - PubMed
Additional references
Giudice 1992
-
- Giudice M, Marra A, Barba A, Passariello N, D'Onofrio F. Hypertrophy of the masseter: a rare case associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Minerva Stomatologica 1992;41(11):535‐42. - PubMed
Harriman 1996
-
- Harriman DG. The histochemistry of reactive masticatory muscle hypertrophy. Muscle and Nerve 1996;19:1447‐56. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Jin Park 2007
-
- Jin Park Y, Woo Jo Y, Bang SI, Kim HJ, Lim SY, Mun GH, et al. Radiofrequency volumetric reduction for masseteric hypertrophy. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery 2007;31(1):42‐52. - PubMed
Kim 2000
-
- Kim HJ, Jeon BS, Lee KW. Hemimasticatory spasm associated with localized scleroderma and facial hemiatrophy. Archives of Neurology 2000;57(4):576‐80. - PubMed
Kitagawa 2000
-
- Kitagawa Y, Hashimoto K, Kuriyama M. Hypertrophic branchial myopathy with uniform predominance of type 1 fibres. Case report. Scandinavian Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery and Hand Surgery 2000;34(4):391‐6. - PubMed
Legg 1880
-
- Legg JW. Enlargement of the temporal and masseter muscles on both sides. Transactions of the Pathological Society of London 1880;31:361‐6.
Newton 1999
-
- Newton JP, Cowpe JG, McClure IJ, Delday MI, Maltin CA. Masseteric hypertrophy?: preliminary report. British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 1999;37(5):405‐8. - PubMed
Nishida 1995
-
- Nishida M, Iizuka T. Intraoral removal of the enlarged mandibular angle associated with masseteric hypertrophy. Journal of Oral Maxillofacial Surgery 1995;53(12):1476‐9. - PubMed
Papapetropoulos 2006
RevMan 2012 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.2. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2012.
Sannomya 2006
-
- Sannomya EK, Gonçalves M, Cavalcanti MP. Masseter muscle hypertrophy: case report. Brazilian Dental Journal 2006;17(4):347‐50. - PubMed
Satoh 2001
-
- Satoh K, Yamaguchi T, Komatsu K, Inoue N, Minowa K, Kanayama T, et al. Analyses of muscular activity, energy metabolism, and muscle fiber type composition in a patient with bilateral masseteric hypertrophy. Cranio 2001;19(4):294‐301. - PubMed
Serrat 1998
-
- Serrat A, Garcia‐Cantera JM, Redondo LM. Isolated unilateral temporalis muscle hypertrophy. A case report. International Journal of Oral Maxillofacial Surgery 1998;27(2):92‐3. - PubMed
Skoura 2001
-
- Skoura C, Mourouzis C, Saranteas T, Chatzigianni E, Tesseromatis C. Masseteric hypertrophy associated with administration of anabolic steroids and unilateral mastication: a case report. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology and Endodontics 2001;92(5):515‐8. - PubMed
Wilson 1990
-
- Wilson PS, Brown AM. Unilateral temporalis muscle hypertrophy: Case report. International Journal of Oral Maxillofacial Surgery 1990;19(5):287‐8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous