Cognitive behavioural therapies for fibromyalgia
- PMID: 24018611
- PMCID: PMC6481397
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009796.pub2
Cognitive behavioural therapies for fibromyalgia
Abstract
Background: Fibromyalgia (FM) is a clinically well-defined chronic condition of unknown aetiology characterized by chronic widespread pain that often co-exists with sleep disturbances, cognitive dysfunction and fatigue. Patients often report high disability levels and negative mood. Psychotherapies focus on reducing key symptoms, improving daily functioning, mood and sense of personal control over pain.
Objectives: To assess the benefits and harms of cognitive behavioural therapies (CBTs) for treating FM at end of treatment and at long-term (at least six months) follow-up.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library 2013, Issue 8), MEDLINE (1966 to 28 August 2013), PsycINFO (1966 to 28 August 2013) and SCOPUS (1980 to 28 August 2013). We searched http://www.clinicaltrials.gov (web site of the US National Institutes of Health) and the World Health Organization Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) (http://www.who.int/ictrp/en/) for ongoing trials (last search 28 August,2013), and the reference lists of reviewed articles.
Selection criteria: We selected randomised controlled trials of CBTs with children, adolescents and adults diagnosed with FM.
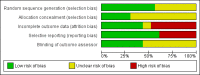
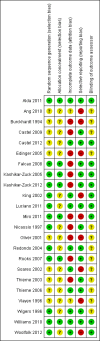
Data collection and analysis: The data of all included studies were extracted and the risks of bias of the studies were assessed independently by two review authors. Discrepancies were resolved by discussion.
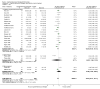
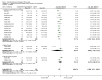
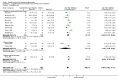
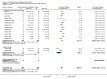
Main results: Twenty-three studies with 24 study arms with CBTs were included. A total of 2031 patients were included; 1073 patients in CBT groups and 958 patients in control groups. Only two studies were without any risk of bias. The GRADE quality of evidence of the studies was low. CBTs were superior to controls in reducing pain at end of treatment by 0.5 points on a scale of 0 to 10 (standardised mean difference (SMD) - 0.29; 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.49 to -0.17) and by 0.6 points at long-term follow-up (median 6 months) (SMD -0.40; 95% CI -0.62 to -0.17); in reducing negative mood at end of treatment by 0.7 points on a scale of 0 to 10 (SMD - 0.33; 95% CI -0.49 to -0.17) and by 1.3 points at long-term follow-up (median 6 months) (SMD -0.43; 95% CI -0.75 to -0.11); and in reducing disability at end of treatment by 0.7 points on a scale of 0 to 10 (SMD - 0.30; 95% CI -0.51 to -0.08) and at long-term follow-up (median 6 months) by 1.2 points (SMD -0.52; 95% CI -0.86 to -0.18). There was no statistically significant difference in dropout rates for any reasons between CBTs and controls (risk ratio (RR) 0.94; 95% CI 0.65 to 1.35).
Authors' conclusions: CBTs provided a small incremental benefit over control interventions in reducing pain, negative mood and disability at the end of treatment and at long-term follow-up. The dropout rates due to any reason did not differ between CBTs and controls.
Conflict of interest statement
WH received honoraria for educational lectures from Abott, Eli‐Lilly, Janssen‐Cilag, Mundipharma and Pfizer. WH serves on the advisory board panel of Daiichi Sankyo. KB received a travel grant from Pfizer and WH from Eli‐Lilly. EC has served on advisory panels of Daiichi Sankyo, Pierre Fabre Medicament, Jazz Pharmaceutical, Allergan and Pfizer. EC has also lectured in meetings organised by Pierre Fabre Medicament, Eli Lilly and Pfizer. The Rheumatology Department of EC received a research grant from Pierre Fabre Medicament. The funding was not used for the production of the review. AB and PK have no conflicts of interest to declare.
None of the authors has done or plans to do a study in this field.
None of the authors received any funding for this review.
Figures















Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Alda 2011 {published and unpublished data}
Ang 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ang DC, Chakr R, Mazzuca S, France CR, Steiner J, Stump T. Cognitive‐behavioral therapy attenuates nociceptive responding in patients with fibromyalgia: a pilot study. Arthritis Care Research (Hoboken) 2010;62:618‐23. - PubMed
Burckhardt 1994 {published data only}
-
- Burckhardt CS, Mannerkopi K, Hedenberg L, Bjelle A. A randomized, controlled clinical trial of education and physical training for women with fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 1994;21:714‐20. - PubMed
Castel 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Castel A, Salvat M, Sala J, Rull M. Cognitive‐behavioural group treatment with hypnosis: A randomized pilot trial in fibromyalgia. Contemporary Hypnosis 2009;26:48‐59.
Castel 2012 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Castel A, Cascón R, Padrol A, Sala J, Rull M. Multicomponent cognitive‐behavioral group therapy with hypnosis for the treatment of fibromyalgia: long‐term outcome. Journal of Pain 2012;13:255‐65. - PubMed
Edinger 2005 {published data only}
-
- Edinger JD, Wohlgemuth WK, Krystal AD, Rice JR. Behavioral insomnia therapy for fibromyalgia patients: a randomized clinical trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 2005;165:2527‐35. - PubMed
Falcao 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Falcao DM, Sales L, Leite JR, Feldman D, Valim V, Natour J. Cognitive‐behavioral therapy for the treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 2008;16:133‐40.
Kashikar‐Zuck 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kashikar‐Zuck S, Swain NF, Jones BA, Graham TB. Efficacy of cognitive‐behavioral intervention for juvenile primary fibromyalgia syndrome. Journal of Rheumatology 2005;32:1594‐602. - PubMed
Kashikar‐Zuck 2012 {published data only}
King 2002 {published data only}
-
- King SJ, Wessel J, Bhambhani Y, Sholter D, Maksymowych W. The effects of exercise and education, individually or combined, in women with fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29:2620‐7. - PubMed
Luciano 2011 {published data only}
-
- Luciano JV, Martínez N, Peñarrubia‐María MT, Fernández‐Vergel R, García‐Campayo J, Verduras C, et al. FibroQoL Study Group. Effectiveness of a psychoeducational treatment program implemented in general practice for fibromyalgia patients: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Journal of Pain 2011;27:383‐91. - PubMed
Miro 2011 {published data only}
-
- Miró E, Lupiáñez J, Martínez MP, Sánchez AI, Díaz‐Piedra C, Guzmán MA, Buela‐Casal G. Cognitive‐behavioral therapy for insomnia improves attentional function in fibromyalgia syndrome: a pilot, randomized controlled trial. Journal of Health Psychology 2011;16:770‐82. - PubMed
Nicassio 1997 {published data only}
-
- Nicassio PM, Radojevic V, Weisman MH, Schuman C, Kim J, Schoenfeld‐Smith K, Krall T. A comparison of behavioral and educational interventions for fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 1997;24:2000‐7. - PubMed
Oliver 2001 {published data only}
-
- Oliver K, Cronan TA, Walen HR, Tomita M. Effects of social support and education on health care costs for patients with fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2001;28:2711‐9. - PubMed
Redondo 2004 {published data only}
-
- Redondo JR, Justo CM, Moraleda FV, Velayos YG, Puche JJ, Zubero JR, et al. Long‐term efficacy of therapy in patients with fibromyalgia: a physical exercise‐based program and a cognitive‐behavioral approach. Arthritis Rheumatism 2004;51:184‐92. - PubMed
Rooks 2007 {published data only}
-
- Rooks DS, Gautam S, Romeling M, Cross ML, Stratigakis D, Evans B, et al. Group exercise, education, and combination self‐management in women with fibromyalgia: a randomized trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 2007;12:2192‐200. - PubMed
Soares 2002 {published data only}
-
- Soares JJF, Grossi G. A randomised, controlled comparison of educational and behavioral interventions for woman with fibromyalgia. Scandinavian Journal of Occupational Therapy 2002;9:35‐45.
Thieme 2003 {published data only}
-
- Thieme K, Gromnica‐Ihle E, Flor H. Operant behavioral treatment of fibromyalgia: a controlled study. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2003;43:314‐20. - PubMed
Thieme 2006 {published and unpublished data}
Vlayen 1996 {published data only}
-
- Vlaeyen JW, Teeken‐Gruben NJ, Goossens ME, Mölken MP, Pett RA, Eek H, Heuts PH. Cognitive‐educational treatment of fibromyalgia: A randomized clinical trial. I. Clinical effects. Journal of Rheumatology 1996;23:1237‐45. - PubMed
Wigers 1996 {published data only}
-
- Wigers SH, Stiles TC, Vogel PA. Effects of aerobic exercise versus stress management treatment in fibromyalgia. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 1996;25:77‐86. - PubMed
Williams 2010 {published data only}
References to studies excluded from this review
Anderson 2007 {published data only}
-
- Anderson FJ, Winkler AE. An integrated model of group psychotherapy for patients with fibromyalgia. International Journal of Group Psychotherapy 2007;57:451‐74. - PubMed
Carleton 2011 {published data only}
-
- Carleton RN, Richter AA, Asmundson GJ. Attention modification in persons with fibromyalgia: a double blind, randomized clinical trial. Cognitive Behaviour Therapy 2011;40:279‐90. - PubMed
De Voogd 2003 {published data only}
-
- Voogd JN, Knipping AA, Blécourt ACE, Rijswijk MH. Treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome with psychomotor therapy and marital counselling. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 2003;1:273‐80.
Garcia 2006 {published data only}
-
- Garcia J, Simon MA, Duran M, Canceller J, Aneiros FJ. Differential efficacy of a cognitive‐behavioral intervention versus pharmacological treatment in the management of fibromyalgic syndrome. Psychology, Health & Medicine 2006;11:498‐50. - PubMed
Goeppinger 2009 {published data only}
-
- Goeppinger J, Lorig KR, Ritter PL, Mutatkar S, Villa F, Gizlice Z. Mail‐delivered arthritis self‐management tool kit: A randomized trial and longitudinal followup. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2009;61:867‐75. - PubMed
Goldenberg 1994 {published data only}
-
- Goldenberg DL, Kaplan KH, Nadeau MG, Brodeur C, Smith S, Schmid CH. A controlled study of stress‐reduction, cognitive‐behavioral treatment program in fibromyalgia. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 1994;2:53‐66.
Haugli 2008 {published data only}
-
- Haugli L, Steen E, Laerum E, Nygard R, Finset A. Pychological distress and employment status. Effects of a group learning programme for patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain. Psychology, Health & Medicine 2003;8:135‐48.
Langford 2010 {published data only}
-
- Langford. The efficacy of a combined cognitive‐behavioural and interpersonal therapy approach to the treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome: A randomized controlled trial. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering 2010;71:2052.
Lommel 2011 {published data only}
-
- Lommel K, Bandyopadhyay A, Martin C, Kapoor S, Crofford L. A pilot study of a combined intervention for management of juvenile primary fibromyalgia symptoms in adolescents in an inpatient psychiatric unit. International Journal of Adolescent Medicine and Health 2011;23:193‐7. - PubMed
Lorig 2008 {published data only}
-
- Lorig KR, Ritter PL, Laurent DD, Plant K. The internet‐based arthritis self‐management program: a one‐year randomized trial for patients with arthritis or fibromyalgia. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2008;15:1009‐17. - PubMed
Martinez‐Valero 2008 {published data only}
-
- Martínez‐Valero C, Castel A, Capafons A, Sala J, Espejo B, Cardeña E. Hypnotic treatment synergizes the psychological treatment of fibromyalgia: a pilot study. The American Journal of Clinical Hypnosis 2008;50:311‐21. - PubMed
Solomon 2002 {published data only}
-
- Solomon DH, Warsi A, Brown‐Stevenson T, Farrell M, Gauthier S, Mikels D, Lee TH. Does self‐management education benefit all populations with arthritis? A randomized controlled trial in a primary care physician network. Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29:362‐8. - PubMed
Stuifbergen 2010 {published data only}
Van Oosterwijck 2013 {published data only}
-
- Oosterwijck J, Meeus M, Paul L, Schryver M, Pascal A, Lambrecht L, Nijs J. Pain Physiology Education Improves Health Status and Endogenous Pain Inhibition in Fibromyalgia: A Double‐Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin J Pain 2013;Jan 30:epub ahead of print. - PubMed
Williams 2002 {published data only}
-
- Williams DA, Cary MA, Groner KH, Chaplin W, Glazer LJ, Rodriguez AM, Clauw DJ. Improving physical functional status in patients with fibromyalgia: a brief cognitive behavioral intervention. Journal of Rheumatology 2002;29:1280‐6. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Jensen 2012 {published data only}
-
- Jensen KB, Kosek E, Wicksell R, Kemani M, Olsson G, Merle JV, et al. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy increases pain‐evoked activation of the prefrontal cortex in patients with fibromyalgia. Pain 2012;153:1495‐503. - PubMed
Martinez 2013 {published data only}
-
- Martínez MP, Miró E, Sánchez AI, Díaz‐Piedra C, Cáliz R, Vlaeyen JW, Buela‐Casal G. Cognitive‐behavioral therapy for insomnia and sleep hygiene in fibromyalgia: a randomized controlled trial. J Behav Med 2013;Jun 7:epub ahead of print. - PubMed
Sanchez 2012 {published data only}
-
- Sanchez A, Diaz‐Piedra C, Miro E, Martinez MP, Galvez R, Buela‐Casal G. Effects of cognitive‐behavioral therapy for insomnia on polysomnographic parameters in fibromyalgia patients. International Journal of Clinical and Health Psychology 2012;12:39‐53.
Wicksell 2012 {published data only}
-
- Wicksell RK, Kemani M, Jensen K, Kosek E, Kadetoff D, Sorjonen K, et al. Acceptance and commitment therapy for fibromyalgia: A randomized controlled trial. European Journal of Pain 2013;17(4):599‐611. - PubMed
Additional references
Altman 2003
Begg 1994
-
- Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994;50(4):1088‐101. - PubMed
Bennett 2006
-
- Bennett R, Nelson D. Cognitive behavioral therapy for fibromyalgia. Nature Clinical Practice. Rheumatology 2006;2:416‐24. - PubMed
Bernardy 2010
-
- Bernardy K, Füber N, Köllner V, Häuser W. Efficacy of cognitive‐behavioral therapies in fibromyalgia syndrome ‐ a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Rheumatology 2010;37(10):1991‐2005. - PubMed
Bernardy 2011
Bliddal 2009
-
- Bliddal H, Christensen R. The treatment and prevention of knee osteoarthritis: a tool for clinical decision‐making. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 2009;10:1793‐804. - PubMed
Brachaniec 2009
Bradley 2009
Branco 2010
-
- Branco JC, Bannwarth B, Failde I, Abello Carbonell J, Blotman F, Spaeth M, et al. Prevalence of fibromyalgia: a survey in five European countries. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism 2010;39(6):448‐53. - PubMed
Brown 2006
Brozek 2009
-
- Brozek JL, Akl EA, Alonso‐Coello P, Lang D, Jaeschke R, Williams JW, et al. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations in clinical practice guidelines. Part 1 of 3. An overview of the GRADE approach and grading quality of evidence about interventions. Allergy 2009;64(5):669‐77. - PubMed
Burckhardt 2005a
-
- Burckhardt CS, Goldenberg D, Crofford L, Gerwin R, Gowans S, Jackson K, et al. Guideline for the management of fibromyalgia syndrome. Pain in adults and children. APS Clinical Practice Guideline Series No. 4. Glenview, IL: American Pain Society, 2005.
Burckhardt 2005b
-
- Burckhardt CS. Educating patients: self‐management approaches. Disability and Rehabilitation 2005;27(12):703‐9. - PubMed
Busch 2007
Carville 2008
-
- Carville SF, Arendt‐Nielsen S, Bliddal H, Blotman F, Branco JC, Buskila D, et al. EULAR evidence based recommendations for the management of fibromyalgia syndrome. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2008;67(4):536‐41. - PubMed
Choi 2010
Cipriani 2009
-
- Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, Geddes JR, Higgins JP, Churchill R. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new‐generation antidepressants: a multiple‐treatments meta‐analysis. Lancet 2009;373(9665):746‐58. - PubMed
Cohen 1988
-
- Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1988.
Dell' Osso 2012
-
- Dell'Osso L, Carmassi C, Consoli G, Conversano C, Ramacciotti CE, Musetti L, et al. Lifetime post‐traumatic stress symptoms are related to the health‐related quality of life and severity of pain/fatigue in patients with fibromyalgia. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2012;29:S73‐8. - PubMed
Dworkin 2008
-
- Dworkin RH, Turk DC, Wyrwich KW, Beaton D, Cleeland CS, Farrar JT, et al. Interpreting the clinical importance of treatment outcomes in chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Journal of Pain 2008;9(2):105‐21. - PubMed
Dworkin 2009
-
- Dworkin RH, Turk DC, McDermott MP, Peirce‐Sandner S, Burke LB, Cowan P, et al. Interpreting the clinical importance of group differences in chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Pain 2009;146(3):238‐44. - PubMed
Eccleston 2009
Eccleston 2012
Egger 1997
Eich 2012
-
- Eich W, Häuser W, Arnold B, Bernardy K, Brückle W, Eidmann U, et al. Fibromyalgia syndrome: General principles and coordination of clinical care and patient education. Schmerz 2012;26:268‐75. - PubMed
Fitzcharles 2012
-
- Fitzcharles MA, Ste‐Marie PA, Goldenberg DL, Pereira JX, Abbey S, Choinière M, et al. 2012 Canadian Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of fibromyalgia syndrome. www.canadianpainsociety.ca/pdf/Fibromyalgia_Guidelines_2012.pdf 2012. - PMC - PubMed
Fordyce 1976
-
- Fordyce WE. Behavioral Methods in Chronic Pain and Illness. St. Louis: Mosby, 1976.
Forseth 1999
-
- Forseth KO, Husby G, Gran JT, Førre O. Prognostic factors for the development of fibromyalgia in women with self‐reported musculoskeletal pain. A prospective study. Journal of Rheumatology 1999;26(11):2458‐67. - PubMed
Furukawa 2006
-
- Furukawa TA, Barbui C, Cipriani A, Brambilla P, Watanabe N. Imputing missing standard deviations in meta‐analyses can provide accurate results. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59:7‐10. - PubMed
Glombiewski 2010
-
- Glombiewski JA, Sawyer AT, Gutermann J, Koenig K, Rief W, Hofmann SG. Psychological treatments for fibromyalgia: a meta‐analysis. Pain 2010;151(2):280‐95. - PubMed
Guyatt 2006
-
- Guyatt G, Gutterman D, Baumann M, Adrizzio‐Harris D, Hylek E, Phillips B, et al. Grading strength of recommendations and quality of evidence in clinical guidelines ‐ Report from an ACCP working group. Chest 2006;129:182‐7. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from http://www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Häuser 2008
-
- Häuser W, Zimmer C, Felde E, Köllner V. What are the key symptoms of fibromyalgia? Results of a survey of the German Fibromyalgia Association [Was sind die Kernsymptome des Fibromyalgiesyndroms? Umfrageergebnisse der Deutschen Fibromyalgievereinigung]. Schmerz 2008;22(2):176‐83. - PubMed
Häuser 2010
-
- Häuser W, Hayo S, Biewer W, Gesmann M, Kühn‐Becker H, Petzke F, et al. Diagnosis of fibromyalgia syndrome ‐ a comparison of Association of the Medical Scientific Societies in Germany, survey, and American College of Rheumatology criteria. Clinical Journal of Pain 2010;26(6):505‐11. - PubMed
Häuser 2011
-
- Häuser W, Kosseva M, Uceyler N, Klose P, Sommer C. Emotional, physical and sexual abuse in fibromyalgia syndrome ‐ a systematic review with meta‐analysis. Arthritis Care and Research 2011;63(6):808‐20. - PubMed
Häuser 2013
Jensen 2011
-
- Jensen MP. Psychosocial approaches to pain management: an organizational framework. Pain 2011;152(4):717‐25. - PubMed
Kashikar‐Zuck 2010
Koulil 2007
Köllner 2012
-
- Köllner V, Häuser W, Klimczyk K, Kühn‐Becker H, Settan M, Weigl M, Bernardy K. Psychotherapy for patients with fibromyalgia syndrome: Systematic review, meta‐analysis and guideline. Schmerz 2012;26:291‐6. - PubMed
Lange 2010
-
- Lange M, Petermann F. Influence of depression on fibromyalgia: a systematic review. Schmerz 2010;24(4):26‐33. - PubMed
Lawrence 2008
Lee 2012
-
- Lee YH, Choi SJ, Ji JD, Song GG. Candidate gene studies of fibromyalgia: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Rheumatology International 2012;32(2):417‐26. - PubMed
Loevinger 2012
Lumley 2011
McBeth 2012
-
- McBeth J, Prescott G, Scotland G, Lovell K, Keeley P, Hannaford P, et al. Cognitive behavior therapy, exercise, or both for treating chronic widespread pain. Archives of Internal Medicine 2012;172:48‐57. - PubMed
Mease 2009
Moore 2010a
-
- Moore AR, Eccleston C, Derry S, Wiffen P, Bell RF, Straube S, et al. "Evidence" in chronic pain‐establishing best practice in the reporting of systematic reviews. Pain 2010;150(3):386‐9. - PubMed
Moore 2010b
-
- Moore RA, Smugar SS, Wang H, Peloso PM, Gammaitoni A. Numbers‐needed‐to‐treat analyses‐‐do timing, dropouts, and outcome matter? Pooled analysis of two randomized, placebo‐controlled chronic low back pain trials. Pain 2010;151:592‐7. - PubMed
Moore 2010c
-
- Moore RA, Derry S, McQuay HJ, Straube S, Aldington D, Wiffen P. Clinical effectiveness: an approach to clinical trial design more relevant to clinical practice, acknowledging the importance of individual differences. Pain 2010;149:173‐6. - PubMed
Moore 2011
Mork 2010
-
- Mork PJ, Vasseljen O, Nilsen TI. Association between physical exercise, body mass index, and risk of fibromyalgia: longitudinal data from the Norwegian Nord‐Trøndelag Health Study. Arthritis Care and Research 2010;62(5):611‐7. - PubMed
Mork 2012
Morley 2011
-
- Morley S. Efficacy and effectiveness of cognitive behaviour therapy for chronic pain: progress and some challenges. Pain 2011;152 Suppl 3:S99‐106. - PubMed
National Institutes of Health 2011
-
- National Institutes of Health. National Centre for Alternative and Complementary Medicine. What Is complementary and alternative medicine?. http://nccam.nih.gov/health/whatiscam (accessed 15 May 2011).
Norman 2001
-
- Norman GR, Sridhar FG, Guyatt GH, Walter SD. Relation of distribution‐ and anchor‐based approaches in interpretation of changes in health‐related quality of life. Medical Care 2001;39(10):1039‐47. - PubMed
Nüesch 2013
-
- Nüesch E, Häuser W, Bernardy K, Barth J, Jüni P. Comparative efficacy of pharmacological and non‐pharmacological interventions in fibromyalgia syndrome: network meta‐analysis. Annals of Rheumatic Diseases 2013;72:955‐62. - PubMed
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Rheumatologist Los Angeles 2012
-
- Rheumatologist Los Angeles. What are the psychological therapies available for fibromyalgia?. http://arthritisconsult.com/fibromyalgia‐doctor/psychological‐treatments... Accessed July 27,2012.
Saxe 2012
-
- Saxe PA, Arnold LM, Palmer RH, Gendreau RM, Chen W. Short‐term (2‐week) effects of discontinuing milnacipran in patients with fibromyalgia. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2012;28:815‐21. - PubMed
Schmidt 2011
-
- Schmidt S, Grossman P, Schwarzer B, Jena S, Naumann J, Walach H. Treating fibromyalgia with mindfulness‐based stress reduction: results from a 3‐armed randomized controlled trial. Pain 2011;152:361‐9. - PubMed
Schulz 2010
Smythe 1981
-
- Smythe HA. Fibrositis and other diffuse musculoskeletal syndromes. In: Kelley WN, Harris Jr ED, Ruddy S, Sledge CB editor(s). Textbook of Rheumatology. First Edition. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1981.
Sommer 2012a
-
- Sommer C, Häuser W, Burgmer M, Engelhardt R, Gerhold K, Petzke F, et al. Etiology and pathophysiology of fibromyalgia syndrome. Schmerz 2012;26(3):259‐67. - PubMed
Sommer 2012b
-
- Sommer C, Häuser W, Alten R, Petzke F, Späth M, Tölle T, et al. Drug therapy of fibromyalgia syndrome: Systematic review, meta‐analysis and guideline. Schmerz 2012;26:297‐310. - PubMed
Theadom 2009
Thieme 2007
-
- Thieme K, Turk DC, Flor H. Responder criteria for operant and cognitive‐behavioral treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2007;57:830‐6. - PubMed
Thieme 2009
-
- Thieme K, Gracely RH. Are psychological treatments effective for fibromyalgia pain?. Current Rheumatology Reports 2009;11(6):443‐50. - PubMed
Thurns 2011
-
- Thorn BE, Burns JW. Common and specific treatment mechanisms in psychosocial pain interventions: the need for a new research agenda. Pain 2011;4:705‐6. - PubMed
Tort 2012
van Koulil 2011
-
- Koulil S, Kraaimaat FW, Lankveld W, Helmond T, Vedder A, Hoorn H, et al. Cognitive‐behavioral mechanisms in a pain‐avoidance and a pain‐persistence treatment for high‐risk fibromyalgia patients. Arthritis Care and Research (Hoboken) 2010;62:1377‐85. - PubMed
Veehof 2011
-
- Veehof MM, Oskam MJ, Schreurs KM, Bohlmeijer ET. Acceptance‐based interventions for the treatment of chronic pain: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Pain 2011;152(3):533‐42. - PubMed
Wampold 2005
-
- Wampold BE, Minami T, Tierney SC, Baskin TW, Bhati KS. The placebo is powerful: estimating placebo effects in medicine and psychotherapy from randomized clinical trials. Journal of Clinical Psychology 2005;61:835‐54. - PubMed
Warsi 2003
-
- Warsi A, LaValley MP, Wang PS, Avorn J, Solomon DH. Arthritis self‐management education programs: a meta‐analysis of the effect on pain and disability. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2003;48(8):2207‐13. - PubMed
Williams 2012
Winkelmann 2011
-
- Winkelmann A, Perrot S, Schaefer C, Ryan K, Chandran A, Sadosky A, et al. Impact of fibromyalgia severity on health economic costs: results from a European cross‐sectional study. Applied Health Economics and Health Policy 2011;9(2):125‐36. - PubMed
Winkelmann 2012
-
- Winkelmann A, Häuser W, Friedel E, Moog‐Egan M, Seeger D, Settan M, et al. Physiotherapy and physical therapies for fibromyalgia syndrome: Systematic review, meta‐analysis and guideline. Schmerz 2012;26:276‐86. - PubMed
Wolfe 1990
-
- Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, Bennett RM, Bombardier C, Goldenberg DL, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 Criteria for the Classification of Fibromyalgia. Report of the Multicenter Criteria Committee. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1990;33(2):160‐72. - PubMed
Wolfe 1997
-
- Wolfe F, Anderson J, Harkness D, Bennett RM, Caro XJ, Goldenberg DL, et al. A prospective, longitudinal, multicenter study of service utilization and costs in fibromyalgia. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1997;40(9):1553‐5. - PubMed
Wolfe 2010
-
- Wolfe F, Clauw DJ, Fitzcharles MA, Goldenberg DL, Katz RS, Mease P, et al. The American College of Rheumatology preliminary diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia and measurement of symptom severity. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2010;62(5):600‐10. - PubMed
Wolfe 2013
-
- Wolfe F, Brähler E, Hinz A, Häuser W. Fibromyalgia prevalence, somatic symptom reporting, and the dimensionality of polysymptomatic distress: results from a survey of the general population. Arthritis Care and Research (Hoboken) 2013;65:777‐85. - PubMed
Yates 2005
-
- Yates SL, Morley S, Eccleston E, Williams A. A scale for rating the quality of psychological trials for pain. Pain 2005;117:314‐25. - PubMed
Yunus 1981
-
- Yunus M, Masi AT, Calabro JJ, Miller KA, Feigenbaum SL. Primary fibromyalgia (fibrositis): clinical study of 50 patients with matched normal controls. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism 1981;11(1):151‐71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

