Isolation of human adipose-derived stromal cells using laser-assisted liposuction and their therapeutic potential in regenerative medicine
- PMID: 24018794
- PMCID: PMC3785265
- DOI: 10.5966/sctm.2012-0183
Isolation of human adipose-derived stromal cells using laser-assisted liposuction and their therapeutic potential in regenerative medicine
Abstract
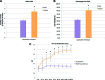
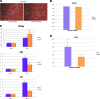
Harvesting adipose-derived stromal cells (ASCs) for tissue engineering is frequently done through liposuction. However, several different techniques exist. Although third-generation ultrasound-assisted liposuction has been shown to not have a negative effect on ASCs, the impact of laser-assisted liposuction on the quality and differentiation potential of ASCs has not been studied. Therefore, ASCs were harvested from laser-assisted lipoaspirate and suction-assisted lipoaspirate. Next, in vitro parameters of cell yield, cell viability and proliferation, surface marker phenotype, osteogenic differentiation, and adipogenic differentiation were performed. Finally, in vivo bone formation was assessed using a critical-sized cranial defect in athymic nude mice. Although ASCs isolated from suction-assisted lipoaspirate and laser-assisted lipoaspirate both successfully underwent osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation, the cell yield, viability, proliferation, and frequency of ASCs (CD34(+)CD31(-)CD45(-)) in the stromal vascular fraction were all significantly less with laser-assisted liposuction in vitro (p < .05). In vivo, quantification of osseous healing by micro-computed tomography revealed significantly more healing with ASCs isolated from suction-assisted lipoaspirate relative to laser-assisted lipoaspirate at the 4-, 6-, and 8-week time points (p < .05). Therefore, as laser-assisted liposuction appears to negatively impact the biology of ASCs, cell harvest using suction-assisted liposuction is preferable for tissue-engineering purposes.
Keywords: Adipose; Adult stem cells; Laser lipoplasty; Liposuction; Stem cell transplantation; Stromal cells.
Figures



References
-
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons 2011 Plastic Surgery Statistics Report. [Accessed December 8, 2012]. Available at http://www.plasticsurgery.org/Documents/news-resources/statistics/2011-s....
-
- Mordon S, Eymard-Maurin AF, Wassmer B, et al. Histologic evaluation of laser lipolysis: Pulsed 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser versus cw 980-nm diode laser. Aesthet Surg J. 2007;27:263–268. - PubMed
-
- Zuk PA. Stem cell research has only just begun. Science. 2001;293:211–212. - PubMed
-
- Aust L, Devlin B, Foster SJ, et al. Yield of human adipose-derived adult stem cells from liposuction aspirates. Cytotherapy. 2004;6:7–14. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto T, Gotoh M, Hattori R, et al. Periurethral injection of autologous adipose-derived stem cells for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy: Report of two initial cases. Int J Urol. 2010;17:75–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

