Interplay of cytoskeletal activity and lipid phase stability in dynamic protein recruitment and clustering
- PMID: 24018870
- PMCID: PMC3767946
- DOI: 10.1038/srep02608
Interplay of cytoskeletal activity and lipid phase stability in dynamic protein recruitment and clustering
Abstract
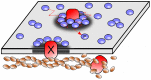
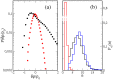
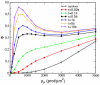
Recent experiments have revealed that some membrane proteins aggregate to form clusters. This type of process has been proven to be dynamic and to be actively maintained by external kinetics. Additionally, this dynamic recruiting is cholesterol- and actin-dependent, suggesting that raft organization and cytoskeleton rearrangement play a crucial role. In the present study, we propose a simple model that provides a general framework to describe the dynamical behavior of lipid-protein assemblies. Our results suggest that lipid-mediated interactions and cytoskeleton-anchored proteins contribute to the modulation of such behavior. In particular, we find a resonant condition between the membrane protein and cytoskeleton dynamics that results in the invariance of the ratio of clustered proteins that is found in in vivo experimental observations.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Membrane nanodomains: contribution of curvature and interaction with proteins and cytoskeleton.Essays Biochem. 2015;57:109-19. doi: 10.1042/bse0570109. Essays Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25658348
-
Inner membrane complex 1l protein of Plasmodium falciparum links membrane lipids with cytoskeletal element 'actin' and its associated motor 'myosin'.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Apr 1;126:673-684. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.239. Epub 2018 Dec 30. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 30599160
-
Integrative Analysis of Subcellular Quantitative Proteomics Studies Reveals Functional Cytoskeleton Membrane-Lipid Raft Interactions in Cancer.J Proteome Res. 2016 Oct 7;15(10):3451-3462. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b01035. Epub 2016 Sep 2. J Proteome Res. 2016. PMID: 27384440
-
Reaction kinetics in the plasma membrane.Biotechnol J. 2012 Jun;7(6):745-52. doi: 10.1002/biot.201100362. Epub 2012 Feb 29. Biotechnol J. 2012. PMID: 22378739 Review.
-
Mesoscale organization of domains in the plasma membrane - beyond the lipid raft.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2018 Apr;53(2):192-207. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2018.1436515. Epub 2018 Feb 18. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29457544 Review.
Cited by
-
Hydroxypropyl‑β‑cyclodextrin attenuates the epithelial‑to‑mesenchymal transition via endoplasmic reticulum stress in MDA‑MB‑231 breast cancer cells.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Jan;21(1):249-257. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10802. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 31746388 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring in vivo cholesterol-mediated interactions between activated EGF receptors in plasma membrane with single-molecule optical tracking.BMC Biophys. 2016 Jun 24;9:6. doi: 10.1186/s13628-016-0030-5. eCollection 2016. BMC Biophys. 2016. PMID: 27347397 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Interleaflet Coupling and Hydrophobic Mismatch in Lipid Membrane Phase-Separation Kinetics.J Am Chem Soc. 2016 Sep 14;138(36):11633-42. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b04880. Epub 2016 Aug 30. J Am Chem Soc. 2016. PMID: 27574865 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of probe diffusion on the SOFI imaging accuracy.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 23;7:44665. doi: 10.1038/srep44665. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28333166 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging FCS delineates subtle heterogeneity in plasma membranes of resting mast cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2020 Mar 19;31(7):709-723. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E19-10-0559. Epub 2020 Jan 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2020. PMID: 31895009 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spira F. et al. Patchwork organization of the yeast plasma membrane into numerous coexisting domains. Nat. Cell Biol. 14, 640–648 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Sharma P. et al. Nanoscale organization of multiple GPI-anchored proteins in living cell membranes. Cell 116, 577–589 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Mayor S. & Rao M. Rafts: scale-dependent, active lipid organization at the cell surface. Traffic Cph. Den. 5, 231–240 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Simons K. & Toomre D. Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1, 31–39 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

