Cinnamon use in type 2 diabetes: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 24019277
- PMCID: PMC3767714
- DOI: 10.1370/afm.1517
Cinnamon use in type 2 diabetes: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Cinnamon has been studied in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) for its glycemic-lowering effects, but studies have been small and show conflicting results. A prior meta-analysis did not show significant results, but several RCTs have been published since then. We conducted an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs evaluating cinnamon's effect on glycemia and lipid levels.
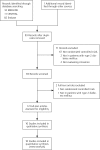
Methods: MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) were searched through February 2012. Included RCTs evaluated cinnamon compared with control in patients with type 2 diabetes and reported at least one of the following: glycated hemoglobin (A1c), fasting plasma glucose, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), or triglycerides. Weighted mean differences (with 95% confidence intervals) for endpoints were calculated using random-effects models.
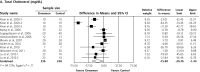
Results: In a meta-analysis of 10 RCTs (n = 543 patients), cinnamon doses of 120 mg/d to 6 g/d for 4 to 18 weeks reduced levels of fasting plasma glucose (-24.59 mg/dL; 95% CI, -40.52 to -8.67 mg/dL), total cholesterol (-15.60 mg/dL; 95% CI, -29.76 to -1.44 mg/dL), LDL-C (-9.42 mg/dL; 95% CI, -17.21 to -1.63 mg/dL), and triglycerides (-29.59 mg/dL; 95% CI, -48.27 to -10.91 mg/dL). Cinnamon also increased levels of HDL-C (1.66 mg/dL; 95% CI, 1.09 to 2.24 mg/dL). No significant effect on hemoglobin A1c levels (-0.16%; 95%, CI -0.39% to 0.02%) was seen. High degrees of heterogeneity were present for all analyses except HDL-C (I(2) ranging from 66.5% to 94.72%).
Conclusions: The consumption of cinnamon is associated with a statistically significant decrease in levels of fasting plasma glucose, total cholesterol, LDL-C, and triglyceride levels, and an increase in HDL-C levels; however, no significant effect on hemoglobin A1c was found. The high degree of heterogeneity may limit the ability to apply these results to patient care, because the preferred dose and duration of therapy are unclear.
Keywords: cinnamon; lipids; meta-analysis; review; systematic; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures





References
-
- Selvin E, Marinopoulos S, Berkenblit G, et al. Meta-analysis: glycosylated hemoglobin and cardiovascular disease in diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 2004;141(6):421–431 - PubMed
-
- Bantle JP, Wylie-Rosett J, Albright AL, et al. ; American Diabetes Association Nutrition recommendations and interventions for diabetes: a position statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(Suppl 1):S61–S78 - PubMed
-
- Ulbricht C, Seamon E, Windsor RC, et al. An evidence-based systematic review of cinnamon (Cinnamomum spp.) by the Natural Standard Research Collaboration. J Diet Suppl. 2011;8(4):378–454 - PubMed
-
- Anand P, Murali KY, Tandon V, Murthy PS, Chandra R. Insulinotropic effect of cinnamaldehyde on transcriptional regulation of pyruvate kinase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, and GLUT4 translocation in experimental diabetic rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2010;186(1):72–81 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
