Cerebral palsy and growth failure at 6 to 7 years
- PMID: 24019415
- PMCID: PMC3784290
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2012-3915
Cerebral palsy and growth failure at 6 to 7 years
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the association between severity of cerebral palsy (CP) and growth to 6 to 7 years of age among children with moderate to severe (Mod/Sev) hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). It was hypothesized that children with Mod/Sev CP would have poorer growth, lower cognitive scores, and increased rehospitalization rates compared with children with no CP (No CP).
Methods: Among 115 of 122 surviving children followed in the hypothermia trial for neonatal HIE, growth parameters and neurodevelopmental status at 18 to 22 months and 6 to 7 years were available. Group comparisons (Mod/Sev CP and No CP) with unadjusted and adjusted analyses for growth <10th percentile and z scores by using Fisher's exact tests and regression modeling were conducted.
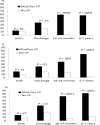
Results: Children with Mod/Sev CP had high rates of slow growth and cognitive and motor impairment and rehospitalizations at 18 to 22 months and 6 to 7 years. At 6 to 7 years of age, children with Mod/Sev CP had increased rates of growth parameters <10th percentile compared with those with No CP (weight, 57% vs 3%; height, 70% vs 2%; and head circumference, 82% vs 13%; P < .0001). Increasing severity of slow growth was associated with increasing age (P < .04 for weight, P < .001 for length, and P < .0001 for head circumference). Gastrostomy feeds were associated with better growth.
Conclusions: Term children with HIE who develop Mod/Sev CP have high and increasing rates of growth <10th percentile by 6 to 7 years of age. These findings support the need for close medical and nutrition management of children with HIE who develop CP.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00005772.
Keywords: cerebral palsy; encephalopathy; growth; hypothermia; hypoxia-ischemia.
Figures
References
-
- de Vries LS, Jongmans MJ. Long-term outcome after neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2010;95(3):F220–F224 - PubMed
-
- Guillet R, Edwards AD, Thoresen M, et al. CoolCap Trial Group . Seven- to eight-year follow-up of the CoolCap trial of head cooling for neonatal encephalopathy. Pediatr Res. 2012;71(2):205–209 - PubMed
-
- Robertson CMT. Long-term follow-up of term infants with perinatal asphyxia. In: Stevenson DK, Sunshine P, Benitz, WE eds. Fetal and Neonatal Brain Injury. 3rd ed. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 2003
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10 HD021385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR80/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10HD21364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021373/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040521/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR008084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040461/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD036790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous